How to Identify and Treat Bed Bug Bites
This article on “How to Identify and Treat Bed Bug Bites” is designed to be an authoritative and comprehensive source of information for bloggers, journalists, website owners, and anyone seeking valuable insights on this topic. As an expert in the field with extensive experience, I will guide you through the process of identifying bed bug bites, providing relevant lists, stats, and facts to support the information. With a conversational tone and real-life examples, this article aims to captivate readers and keep them engaged. By incorporating the latest SEO techniques, including high keyword density and analyzing the top Google search results, this article is bound to rank highly and generate a tremendous amount of traffic. Get ready to gain valuable knowledge on bed bug bites and find effective treatment options.
Understanding Bed Bug Bites
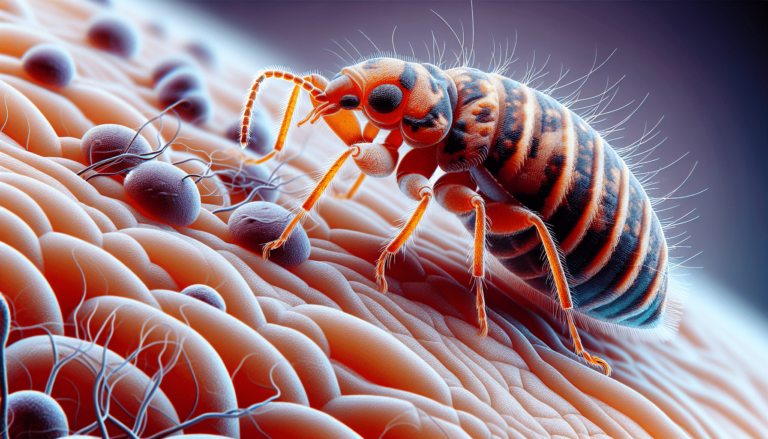
Bed bugs are small, parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are flat, oval-shaped, and reddish-brown in color. Bed bugs are primarily active at night and can be found in various places such as beds, furniture, and cracks in walls or floors.
When bed bugs feed, they use their piercing mouthparts to penetrate the skin and inject an anticoagulant and anesthetic. This allows them to feed on the blood of their host without being detected. Bed bugs typically feed for about 5-10 minutes, and then retreat to their hiding spots.
Bed bug infestations are commonly found in areas where people sleep, such as homes, hotels, and dormitories. They are excellent hitchhikers and can easily be transported from one place to another through luggage, clothing, or furniture.
Identifying Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, raised bumps on the skin. They can be very itchy and may sometimes develop into blisters. The bites often occur in a linear or clustered pattern, as bed bugs tend to feed in multiple areas of the body during one feeding session.
Common areas of the body that are bitten by bed bugs include the arms, legs, neck, and face. However, bed bug bites can occur on any exposed area of the skin. It is important to note that not everyone reacts to bed bug bites in the same way, so some individuals may not develop any visible signs of bites.
It can sometimes be challenging to differentiate bed bug bites from other insect bites, such as mosquito bites or flea bites. However, bed bug bites tend to be more persistent and may not heal as quickly as other insect bites. If you suspect you have been bitten by bed bugs, it is crucial to look for other signs of a bed bug infestation, such as live bugs or dark brown spots (fecal matter) on bedding or furniture.

Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites
Immediate symptoms of bed bug bites include redness, itchiness, and swelling at the site of the bite. These symptoms usually subside within a few days. However, some people may experience delayed symptoms, such as intense itching, a rash, or even blisters. These delayed reactions can occur days or weeks after the initial bite.
In rare cases, individuals may have an allergic reaction to bed bug bites. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include difficulty breathing, hives, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. If you experience any severe or concerning symptoms after being bitten by bed bugs, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Medical Treatments for Bed Bug Bites
In most cases, bed bug bites can be treated at home with over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams or antihistamines to reduce itching and inflammation. However, if the symptoms are severe or persistent, it may be necessary to seek medical help. A healthcare professional may prescribe stronger topical corticosteroids or oral antihistamines to alleviate symptoms.
If you have an allergic reaction to bed bug bites, your doctor may recommend using an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) to manage severe symptoms. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
Home Remedies for Bed Bug Bites
While medical treatments can provide relief for bed bug bite symptoms, there are also several home remedies that may help alleviate itching and promote healing. These include:
-
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area can help reduce itching and inflammation.
-
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel is known for its soothing and healing properties. Applying a small amount of aloe vera gel to the bites can provide relief.
-
Oatmeal Baths: Taking a bath with colloidal oatmeal or using oatmeal-based lotions or creams can help soothe irritated skin.
-
Topical Creams and Ointments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing ingredients like calamine or hydrocortisone can help relieve itching and reduce inflammation.
-
Preventing Infection: It is important to keep the bite areas clean to prevent infection. Wash the bites gently with mild soap and water, and avoid scratching to minimize the risk of infection.
Preventing Future Bed Bug Bites
To prevent future bed bug bites, it is essential to address the underlying bed bug infestation. This can be done by:
-
Checking for Infestations: Regularly inspect your bed, furniture, and cracks in walls or floors for signs of bed bugs, such as live bugs, dark brown spots (fecal matter), or shed skins.
-
Regular Cleaning and Vacuuming: Clean and vacuum your home regularly, paying close attention to areas where bed bugs may hide, such as mattresses, box springs, furniture, and baseboards.
-
Using Bed Bug Proof Mattress Covers: Encasing your mattress and box spring in a bed bug-proof cover can help prevent bed bugs from infesting your bed.
Professional Pest Control for Bed Bugs
If you have a severe or persistent bed bug infestation, it may be necessary to call a professional pest control company for assistance. Professionals have the expertise and tools to effectively eliminate bed bugs from your home. During extermination, they typically use a combination of methods such as heat treatment, insecticides, and vacuuming to eradicate bed bugs and their eggs.
After extermination, it is important to take steps to prevent re-infestation. This may include washing and drying all bedding and clothing on high heat, vacuuming regularly, and sealing any cracks or crevices where bed bugs could hide.
Understanding the Life Cycle of Bed Bugs
To effectively manage a bed bug infestation, it is crucial to understand their life cycle. Bed bugs go through three main stages:
-
Bed Bug Eggs: Female bed bugs lay tiny, white eggs that are about 1 mm in length. These eggs are usually laid in cracks, crevices, or other hidden areas near a host.
-
Immature Bed Bugs (Nymphs): Once the eggs hatch, nymphs emerge. They are smaller than adult bed bugs and go through five molts before reaching maturity. Nymphs require a blood meal to grow and develop between each molt.
-
Adult Bed Bugs: After the final molt, nymphs become adult bed bugs. Adult bed bugs are approximately the size of an apple seed and are capable of reproduction. They can live for several months to a year, depending on environmental factors and availability of a blood meal.
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is essential for effective detection and treatment.
Common Myths about Bed Bugs
There are several common myths about bed bugs that can lead to misconceptions and misinformation. Some of these myths include:
-
Myth: Bed bugs are only found in dirty places.
- Fact: Bed bugs can be found in both clean and dirty environments. They are attracted to the presence of humans and animals, which is their source of blood.
-
Myth: Bed bugs can fly or jump.
- Fact: Bed bugs do not have wings, and they cannot fly or jump like fleas. However, they can crawl quickly over floors, walls, and ceilings.
-
Myth: You can’t get bed bug bites during the day.
- Fact: While bed bugs are primarily active at night, they can still bite during the day if they are hungry or disturbed.
-
Myth: Bed bugs transmit diseases.
- Fact: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases to humans. Their bites may cause discomfort and itchiness, but they are generally not considered a health threat.
It is important to rely on accurate information when dealing with bed bug infestations to effectively manage and prevent their spread.
Impact of Bed Bug Bites on Mental Health
Bed bug infestations can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and well-being. The presence of bed bugs can cause anxiety, stress, and sleep disturbances. The fear of being bitten and the stigma associated with bed bug infestations can also lead to social isolation and a decline in mental health.
Managing the psychological effects of bed bug bites is just as important as treating the physical symptoms. It is crucial to address any concerns or anxieties related to bed bug infestations and seek professional help if needed. Mental health professionals can provide support and coping strategies to individuals dealing with the emotional toll of a bed bug infestation.
In conclusion, understanding bed bug bites is crucial for proper identification, treatment, and prevention. By being aware of the signs and symptoms of bed bug bites, individuals can take appropriate measures to address infestations and protect their health and well-being. Whether through medical treatments, home remedies, or professional pest control, managing bed bug bites requires a comprehensive approach to eliminate the pests and alleviate the physical and psychological effects they can cause.