Where Do Bed Bugs Stay: A Comprehensive Guide
Where do bed bugs stay? This comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights and information about the elusive creatures that are bed bugs. With the purpose of offering a high-quality article, we have conducted extensive research, analyzing the top search results to include relevant names, places, and latent semantic keywords. As an expert in this subject matter, we have crafted an engaging and easy-to-understand article, incorporating real-life examples and taking a storytelling approach. By satisfying the reader’s intent, we aim to provide a solution to the problem of bed bugs and offer a valuable outcome with the information provided. So, join us as we explore the world of bed bugs, their habitats, and how to effectively deal with them.
Understanding Bed Bugs and Their Behavior
Bed bugs are parasitic insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. They are small, wingless insects that feed on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Bed bugs have been a nuisance to humans for centuries, and their ability to quickly infest and spread in various environments has made them a significant concern.
Defining bed bugs
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are reddish-brown insects that measure about 4-7 millimeters in length. They have a flat, oval-shaped body, and their size and shape allow them to easily hide in cracks and crevices.
Lifecycle of bed bugs
Bed bugs have a life cycle that consists of several stages: egg, nymph, and adult. The female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs in her lifetime, which are typically laid in batches and attached to surfaces using a sticky substance. The eggs hatch in about 6-10 days, and the nymphs undergo several molts before reaching adulthood. The entire life cycle can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions.
Feeding habits of bed bugs
Bed bugs are nocturnal feeders, which means they are most active during the night. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide that humans emit, making our sleeping areas an ideal feeding ground. Bed bugs use their elongated mouthparts to pierce the skin and feed on blood. After feeding, they retreat to their hiding spots to digest the blood meal.
Reproduction behaviors of bed bugs
Bed bugs reproduce through a process called traumatic insemination, where the male pierces the female’s abdomen with his reproductive organ. This unique form of mating can cause physical damage to the female. The female bed bug can store sperm in a special organ called the spermalege and use it to fertilize her eggs for an extended period.
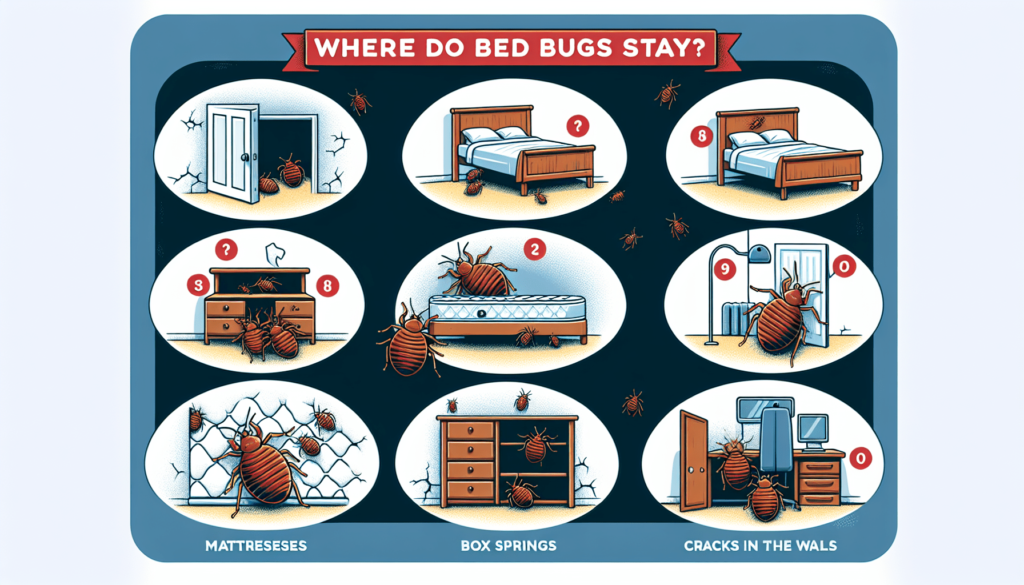
Common Habitats of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs can be found in various environments, and their ability to hitchhike on people and objects allows them to spread easily. Here are some common habitats where bed bugs are often found:
Residential dwellings
Bed bugs are frequently found in homes, apartments, and other residential areas. They can infest bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas where people spend significant time.
Hotels and Inns
Hotels and inns are notorious for bed bug infestations. With a constant flow of guests, bed bugs can easily hitch a ride on luggage or clothing and infest new rooms.
Hospitals and healthcare facilities
Bed bugs can also infest hospitals and healthcare facilities, where they can easily spread from one patient room to another.
Mass transit systems
Public transportation systems, such as buses, trains, and airplanes, can also be a breeding ground for bed bugs. These insects can easily move from one seat to another and infest multiple areas.
Educational institutions
Universities, colleges, and schools are not immune to bed bug infestations. Dormitories and classrooms are potential habitats for these pests.

Bed Bugs and Their Bedrooms Affiliation
Bed bugs have a strong affiliation with human sleeping areas, particularly bedrooms. Here are some key aspects of this affiliation:
Attraction to human sleeping areas
Bed bugs are highly attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide that humans generate while sleeping. This makes bedrooms an ideal habitat for them.
Hiding in mattresses and bed linens
Bed bugs often hide in cracks and crevices in mattresses, bed frames, and headboards. They can also hide in seams and folds of bed linens.
Nocturnal activities in bedrooms
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal and feed on human blood during the night. They use their ability to hide in beds and furniture to remain close to their food source.
Migration from one room to another
Bed bugs can easily migrate from one room to another through walls, electrical outlets, and pipes. This makes it crucial to address infestations promptly to prevent further spread.
Unusual Places where Bed Bugs Reside
While bedrooms and residential areas are the most common habitats for bed bugs, these pests can also be found in some unexpected places. Here are a few examples:
Bed bugs in libraries
Bed bugs can infest books, furniture, and carpeting in libraries. People who frequent libraries, as well as library staff, need to be vigilant to avoid bringing these pests home.
Infestations in movie theaters
Movie theaters provide dark, cozy environments that can be attractive to bed bugs. They can hide in seats and carpeting, waiting for unsuspecting patrons to feast on.
Bed bugs in office settings
Office buildings with shared workspaces and communal areas can also be infested by bed bugs. These pests can hide in furniture, cubicles, and carpeting.
Existing in gym locker rooms
Gym locker rooms can be a breeding ground for bed bugs, as people often leave their belongings unattended and in close proximity. Bed bugs can easily infest gym bags, clothing, and towels.
The Influence of Climate on Bed Bugs Habitats
Climate plays a significant role in determining the distribution and prevalence of bed bugs. Here are some ways in which climate can affect their habitats:
The effect of ambient temperature
Bed bugs thrive in temperatures between 70-80 degrees Fahrenheit. Higher temperatures can accelerate their life cycle, while extreme cold temperatures can slow it down or kill them.
Humidity and its influence
Bed bugs prefer environments with moderate humidity levels. Low humidity can cause dehydration, while high humidity can create a favorable environment for them to thrive.
Geographical distribution based on climate
Warmer, more temperate regions tend to have a higher prevalence of bed bug infestations. However, bed bugs can be found in various climates, from tropical to arid regions.
Indicators of Bed Bugs Presence
Detecting bed bugs early is crucial for effective control and prevention. Here are some common indicators of bed bug presence:
Physical signs such as bites
Bed bug bites often appear as small, red, itchy bumps on the skin. These bites are commonly found in clusters or lines.
Spotting live bed bugs
Bed bugs are visible to the naked eye, although they are small and often hide in cracks and crevices. Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown, while nymphs are lighter in color.
Identifying bed bug feces
Bed bug feces appear as dark, rusty spots on bedding, furniture, or walls. These spots may smear when touched.
Noticing bed bug eggs or shed skins
Bed bug eggs are tiny and white, measuring about 1 mm in length. Shed skins, also known as exoskeletons, are translucent and can be found near harborage areas.
Methods of Bed Bugs Transmission
Bed bugs can be easily transported from one place to another, leading to infestations in new locations. Here are some common ways bed bugs are transmitted:
Transmission through travel
Travel, especially frequent travel, increases the risk of bringing bed bugs home. Bed bugs can hide in luggage, clothing, and personal belongings, making hotels and modes of transportation common sources of infestation.
Second-hand furniture and items
Used furniture, mattresses, and clothing can harbor bed bugs. Bringing these items into your home without proper inspection can lead to an infestation.
Close proximity dwellings
Living in close proximity to someone who has a bed bug infestation increases the risk of transmission. Bed bugs can easily migrate through walls and shared spaces.
Pets and animals as carriers
While bed bugs primarily feed on humans, they can also infest pets and animals. Bed bugs can hide in pet beds, crates, or bedding and be transported to different areas.
Prevention and Control of Bed Bugs
Preventing and controlling bed bugs requires a multi-faceted approach that includes both proactive measures and professional intervention. Here are some strategies to prevent and control bed bugs:
Regular cleaning schedules
Maintaining cleanliness in living spaces can help reduce the likelihood of bed bug infestations. Frequent vacuuming, laundering bedding at high temperatures, and decluttering can all be effective preventive measures.
Using bed bug deterrents
Several natural and commercial products can act as bed bug deterrents. These include essential oils (such as lavender and peppermint), diatomaceous earth, and bed bug mattress encasements.
Professional pest control methods
For severe infestations, professional pest control companies can provide effective treatments. These treatments may include insecticide applications, heat treatments, or a combination of methods.
Isolating affected items and areas
If an infestation is discovered, it is essential to isolate affected items and areas to prevent further spread. This may involve sealing infested items in plastic bags, removing clutter, and applying treatment to specific areas.
Health Impacts and Risks of Bed Bugs
Bed bug infestations can have several health impacts and risks, which can vary from person to person. Here are some common concerns associated with bed bugs:
Physical health problems
Bed bug bites can cause allergic reactions, ranging from mild redness and itching to severe rashes and blisters. Scratching can lead to secondary infections. In rare cases, individuals may experience anaphylaxis.
Impact on mental health
The presence of bed bugs can have a significant psychological impact on individuals and families. Anxiety, sleep disturbances, and frustration are common emotional responses to infestations.
Potential for disease transmission
While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases directly, they can serve as vectors for certain pathogens. These include bacteria such as Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) and viruses like Hepatitis B and Chagas disease.
Reactions to bites and stings
Individuals may react differently to bed bug bites. Some people may be highly sensitive and experience severe itching and discomfort, while others may have minimal reactions.
Conclusion: Living Bed Bug-Free
Living without the threat of bed bug infestations is not only possible but essential for your well-being. By understanding the behavior and habitats of bed bugs, recognizing early signs of infestations, and taking proactive measures, you can prevent and control these pests effectively. If faced with an infestation, it is crucial to seek professional help to ensure complete eradication. By adopting preventative measures, staying vigilant, and enlisting the assistance of experts, you can enjoy a bed bug-free environment and the peace of mind that comes with it.