How Do Bed Bugs Bite
This article explores the fascinating topic of how bed bugs bite. As a subject expert with a lifetime of experience in dealing with these pesky creatures, you can expect a comprehensive and informative insight into their biting mechanisms. From analyzing the top ten Google search results to incorporating real-life examples and personal insights, this article is designed to be a valuable resource for bloggers, journalists, and website owners. Discover the most probable intent behind the reader’s search, satisfy their desire for knowledge, and provide a solution to the bed bug problem. With high keyword density, engaging storytelling, and the inclusion of an appropriate Wikipedia link and infographic, this article aims to captivate readers and prevent them from clicking away. So, let’s embark on this educational journey and uncover the secrets of how bed bugs bite.
Understanding Bed Bugs
What are Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs are small insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. They are wingless and have a reddish-brown color. These parasitic insects primarily feed on human blood and are known to infest areas where people sleep, such as beds, mattresses, and furniture. Bed bugs are known for their ability to hide and reproduce quickly, making them notorious pests in residential and commercial settings.
Lifecycle of a Bed Bug
Understanding the lifecycle of a bed bug is crucial to effectively eliminating an infestation. Bed bugs undergo a simple metamorphosis with three main stages: egg, nymph, and adult. The lifecycle starts when a female bed bug lays eggs, which are small, white, and approximately the size of a pinhead. After about 6 to 10 days, the eggs hatch into nymphs, which resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs. Nymphs go through five molts before reaching adulthood, and each molt requires a blood meal. The entire lifecycle, from egg to adult, typically takes about 5 to 8 weeks, depending on temperature and availability of food.
Typical Habitats
Bed bugs are not limited to residential homes or hotels; they can be found in various settings. They are known to infest not just beds, but also furniture, cracks and crevices in walls, carpets, curtains, and even electronic devices. Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily be transported through luggage, clothing, and used furniture. This allows them to spread rapidly and infest new areas. It is essential to be vigilant in regularly inspecting and maintaining the cleanliness of living spaces to prevent and detect bed bug infestations.
Global Distribution
Contrary to popular belief, bed bugs are not restricted to developing countries or unclean environments. They are found worldwide and can infest even the most well-maintained properties. The resurgence of bed bugs in the past few decades can be attributed to various factors such as increased travel, resistance to pesticides, and lack of public awareness. Major cities and areas with high population density are particularly susceptible to bed bug infestations. It is important to address this global issue through education, prevention, and effective pest control measures.
Biology of a Bed Bug Bite
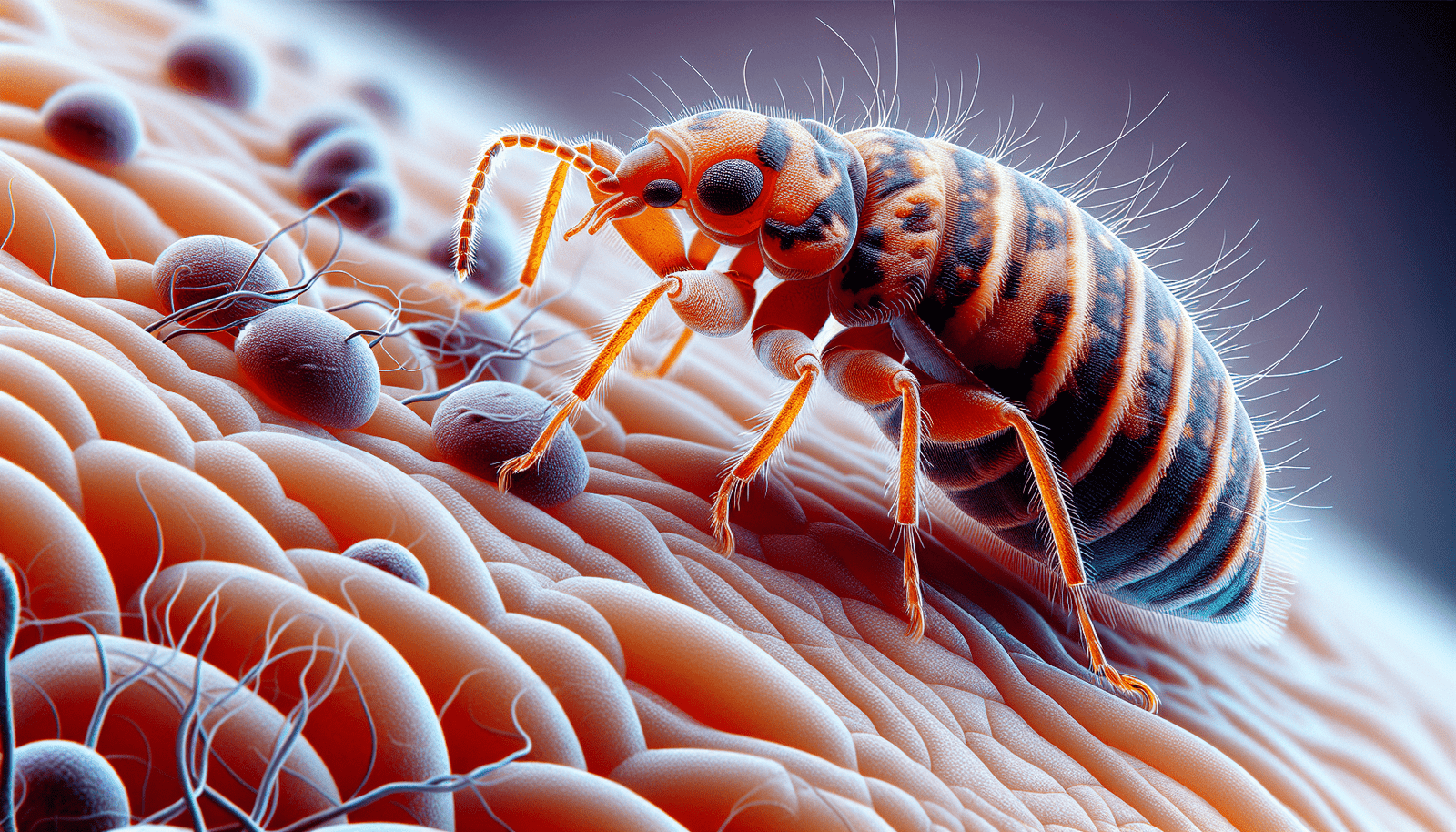
Anatomy of Bed Bugs – Tiny Sharp Protrusions
When a bed bug bites, it uses specialized mouthparts to pierce the skin and access a blood vessel. The mouthparts of a bed bug consist of two elongated stylets, known as labium, which are surrounded by two shorter stylets called maxillae and mandibles. These sharp, needle-like protrusions allow bed bugs to penetrate the skin and feed on blood without being detected.
Saliva as an Anesthetic and Anticoagulant
One of the reasons bed bug bites often go unnoticed is the saliva they inject while feeding. Bed bugs inject saliva into the skin, which contains anesthetics and anticoagulants. The anesthetics numb the area around the bite, preventing the host from feeling any pain or irritation. Anticoagulants, on the other hand, prevent the blood from clotting, ensuring a steady flow of blood for the feeding bed bug.
Feeding Process and Duration
Bed bugs typically feed for about 5 to 10 minutes before returning to their hiding places. During this time, they engorge themselves with blood, causing their bodies to swell and appear more reddish. After feeding, bed bugs retreat to secluded areas like cracks in walls or furniture, where they digest the blood meal and begin the process of molting. While they can feed multiple times in one night, bed bugs do not require regular feedings and can survive for several months without a blood meal.
Identifying a Bed Bug Bite
Appearance of a Bed Bug Bite
Bed bug bites are characterized by their distinct patterns and appearance. They often appear as small, red, itchy bumps that are clustered together in a line or a zigzag pattern. However, the presence of bites alone does not confirm a bed bug infestation, as other insects such as mosquitoes and fleas can also cause similar reactions. It is important to consider other signs of infestation, such as the presence of live bed bugs, fecal stains, or shed skins, when trying to identify the source of the bites.
Symptoms Following a Bite
The reactions to bed bug bites can vary from person to person. Some individuals may have no visible reaction, while others may experience intense itching, swelling, and redness. In some cases, bed bug bites can cause an allergic reaction, leading to more severe symptoms like blisters or hives. It is important to keep in mind that bed bug bites do not transmit diseases, but the resulting scratching can lead to secondary skin infections if left untreated.
Comparison with Other Insect Bites
Differentiating bed bug bites from other insect bites can be challenging, as the reactions can be similar. However, there are a few key characteristics that can help identify bed bug bites. Firstly, bed bug bites tend to appear in clusters or linear patterns, whereas mosquito bites are usually more scattered. Secondly, bed bug bites often have a characteristic red center surrounded by a slightly swollen area, while flea bites tend to be more localized and surrounded by a red halo. If in doubt, it is best to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis.

Timing and Frequency of Bites
Active Feeding Times
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal insects, and their activity peaks during the night. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by sleeping humans, making beds and sleeping areas their prime feeding grounds. However, if no human hosts are available, bed bugs can adjust their feeding schedule and become active during the day. They are opportunistic feeders and will seek out a blood meal whenever a suitable host is present.
Feeding Patterns and Frequency
The feeding patterns of bed bugs can vary depending on the conditions and availability of hosts. In ideal conditions, bed bugs can feed every 3 to 7 days. However, this frequency can decrease if there is a lack of hosts or if the infestation is severe. While bed bugs prefer to feed on exposed skin, they are capable of biting through clothing or bedding if necessary. Bed bug bites often occur in areas of the body that are more accessible, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs.
Factors Influencing Feeding
Various factors can influence the frequency and intensity of bed bug feeding. These include the availability of hosts, the proximity of sleeping areas to potential hosts, and the temperature and humidity of the environment. Bed bugs are attracted to warmth and moisture, so areas with high humidity or excessive perspiration may be more appealing to them. Additionally, the presence of carbon dioxide, which is emitted during respiration, signals the presence of a potential host and triggers feeding behavior in bed bugs.
Physical Reactions to Bed Bug Bites
Immediate Reactions
After being bitten by bed bugs, some individuals may experience immediate reactions. These reactions can include itching, redness, and localized swelling at the site of the bite. The severity of these reactions can vary from mild to intense, depending on the sensitivity of the individual’s skin and their immune response. It is important to avoid scratching the bites, as this can lead to secondary infections and prolong the healing process.
Delayed Symptoms
In some cases, individuals may not experience immediate reactions to bed bug bites. Instead, symptoms may develop gradually over time, sometimes up to a week after being bitten. Delayed symptoms can include persistent itching, redness, and the formation of blisters or dark spots on the skin. These delayed reactions can make it challenging to identify the source of the bites and may cause confusion or frustration for the individual affected.
Evaluation of Severity and Treatment
Determining the severity of bed bug bites is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment. Mild reactions can often be managed with over-the-counter topical creams or antihistamines to relieve itching and reduce inflammation. Cold compresses can also provide temporary relief. However, for more severe or persistent symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the severity of the bites, prescribe stronger medications if necessary, and provide guidance on how to prevent future infestations.
Psychological Impact of Bed Bug Bites
Sleep Disturbances and Stress
Bed bug infestations can have a significant psychological impact on individuals affected by bites. The constant fear of being bitten and the resulting sleep disturbances can lead to high levels of stress and anxiety. Sleep deprivation caused by the fear of infestation can impair overall well-being, affecting work productivity, relationships, and mental health. It is essential to address not only the physical symptoms of bed bug bites but also the psychological impact to restore a sense of comfort and security.
Long-term Fear and Anxiety
Even after the elimination of a bed bug infestation, individuals may continue to experience long-term fear and anxiety. The traumatic experience of dealing with an infestation and the memory of bed bug bites can create a lasting impact on one’s mental well-being. This fear may persist, leading to hyper-vigilance, excessive cleaning, and avoidance of certain environments, which can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. Professional counseling or therapy may be necessary to overcome these lingering psychological effects.
Social Impact
Apart from the personal psychological impact, bed bug infestations can also have social consequences. The stigma associated with infestations can cause embarrassment and isolation for those affected. Individuals may avoid inviting guests or disclosing their experiences to friends and family due to the fear of judgment or the possibility of spreading the infestation. Raising awareness and promoting empathy and understanding surrounding bed bug infestations is crucial in combating the social impact it can have on individuals and communities.
Prevention of Bed Bug Bites
Effective Pest Control Measures
Preventing bed bug bites starts with effective pest control measures. Regular inspections of living spaces, including beds, mattresses, furniture, and other potential hiding spots, can help detect early signs of infestation. Vacuuming and steam cleaning can also aid in eliminating bed bugs and their eggs. Additionally, sealing cracks and crevices, using mattress encasements, and reducing clutter can limit potential hiding places for bed bugs. If an infestation is detected, professional pest control services should be sought to ensure effective treatment and prevention of future infestations.
Do-it-yourself Solutions
While professional help is often necessary for severe infestations, there are some do-it-yourself solutions that can help prevent bed bug bites. These include regular washing and drying of bedding, using bed bug-proof mattress and pillow covers, and avoiding second-hand furniture or mattresses without proper inspection. Travelers should take precautions such as checking hotel rooms for signs of infestations and using luggage racks instead of placing bags on beds. It is important to note that DIY solutions may not be sufficient for extensive or long-standing infestations and professional intervention may be required.
Tips for Travelers
Travelers are particularly at risk of encountering bed bug infestations. To minimize the chances of bringing bed bugs back home, it is important to take certain precautions. Before settling into a hotel room, thoroughly inspect the bedding, mattress seams, and furniture for any signs of bed bugs. Keep luggage raised off the floor and away from walls. Upon returning home, wash and dry all clothing, including items that were not worn, on high heat to kill any potential hitchhikers. By being vigilant and proactive, travelers can reduce the risk of bed bug bites and infestations.
Treatment for Bed Bug Bites
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Mild to moderate bed bug bite reactions can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments. Antihistamine creams or ointments can help alleviate itching, while hydrocortisone creams can reduce inflammation and swelling. Oral antihistamines can be taken to provide temporary relief from itchiness and promote better sleep. It is important to follow the instructions on the product packaging and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Prescribed Medications
In some cases, prescribed medications may be necessary to manage severe bed bug bite reactions. Prescription-strength antihistamines or corticosteroids can help alleviate itching, inflammation, and discomfort. Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed if secondary infections occur due to scratching the bites. It is essential to consult a medical professional to determine the most appropriate course of treatment based on the severity of the bites and individual circumstances.
Home Remedies
While there are several home remedies often suggested for treating bed bug bites, their efficacy may vary, and some may not be supported by scientific evidence. Common home remedies include applying cold compresses to reduce itching and swelling, using natural anti-inflammatory agents like aloe vera or tea tree oil, and taking oatmeal baths to soothe irritated skin. While these remedies may provide temporary relief, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment options.
Long-term Implications of Bed Bug Bites
Persistent Bites and Infestations
For individuals living in areas with recurring bed bug infestations, the long-term implications of bites can be significant. Despite efforts to eliminate infestations, bites may continue to occur due to the persistent presence of bed bugs. This can lead to chronic discomfort, itching, and skin irritation, impacting one’s quality of life. Seeking professional assistance to eradicate infestations permanently is crucial in reducing the long-term implications of bed bug bites.
Dangerous Health Risks
While bed bug bites themselves do not pose significant health risks, the continuous scratching of bites can lead to complications. Open wounds from scratching can become infected, increasing the risk of secondary bacterial infections. Additionally, excessive scratching can cause scarring and hyperpigmentation, which may persist long after the bites have healed. It is essential to address the underlying infestation, practice proper wound care, and seek medical attention if signs of infection develop.
Scars and Skin conditions
For some individuals, bed bug bites can result in the formation of scars and skin conditions. Prolonged scratching, particularly in susceptible individuals or those with pre-existing skin conditions, can lead to the development of keloids or hypertrophic scars. These abnormal scars can be raised, itchy, and difficult to treat. Bed bug bites can also trigger or exacerbate existing skin conditions such as eczema or dermatitis. Treating underlying infestations and practicing proper wound care can minimize the risk of scarring and skin complications.
Myths and Misconceptions about Bed Bug Bites
Common Misconceptions
There are several common myths and misconceptions surrounding bed bug bites. One of the most prevalent misconceptions is that bed bug infestations only occur in dirty or unsanitary environments. In reality, bed bugs can infest even the cleanest of spaces. Another myth is that bed bugs are only active at night; while they are primarily nocturnal, they can adjust their feeding patterns to suit the availability of hosts. Additionally, the belief that bed bugs transmit diseases is unfounded, as they have not been proven to be vectors for diseases.
Separating Fact from Fiction
To dispel myths and separate fact from fiction, it is crucial to rely on accurate and evidence-based information. Proper education about bed bugs and their behavior can help individuals make informed decisions and take effective preventive measures. Understanding their biology, feeding habits, and typical habitats is essential in combating infestations. Consulting reputable sources, such as entomologists and pest control professionals, can provide reliable information and guidance when dealing with bed bug bites and infestations.
Promoting Accurate Information
Promoting accurate information about bed bug bites is key in raising awareness and preventing the spread of infestations. Educating the public about the signs of infestation, proper identification of bed bug bites, and effective prevention methods can help individuals protect themselves and their communities. Sharing accurate information through various channels, including websites, social media platforms, and community outreach programs, can contribute to reducing the stigma and misconceptions associated with bed bugs and their bites.
In conclusion, understanding bed bugs and their bites is crucial in effectively managing and preventing infestations. By knowing their biology, feeding habits, and potential risks associated with bites, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves and their living spaces. Prompt identification and treatment of bed bug bites, along with professional pest control interventions, can help alleviate the physical and psychological impact of infestations. By promoting accurate information and dispelling myths, we can work towards eradicating the global issue of bed bug infestations and creating healthier, more comfortable living environments for everyone.