10 Things You Need to Know About Bed Bugs
This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of bed bugs and equip you with the necessary knowledge to effectively deal with these pesky insects. From the perspective of a seasoned expert in the field, we will delve into the top ten things you need to know about bed bugs. By incorporating a conversational tone and real-life examples, we will ensure that the content is engaging and easy to comprehend. Using data, statistics, and expert sources, we will present you with helpful information that is both unique and valuable. Whether you are a blogger, journalist, website owner, or simply someone seeking information on bed bugs, this article will fulfill your desire to gain insight into these notorious creatures and their impact on human lives.

What are Bed Bugs?
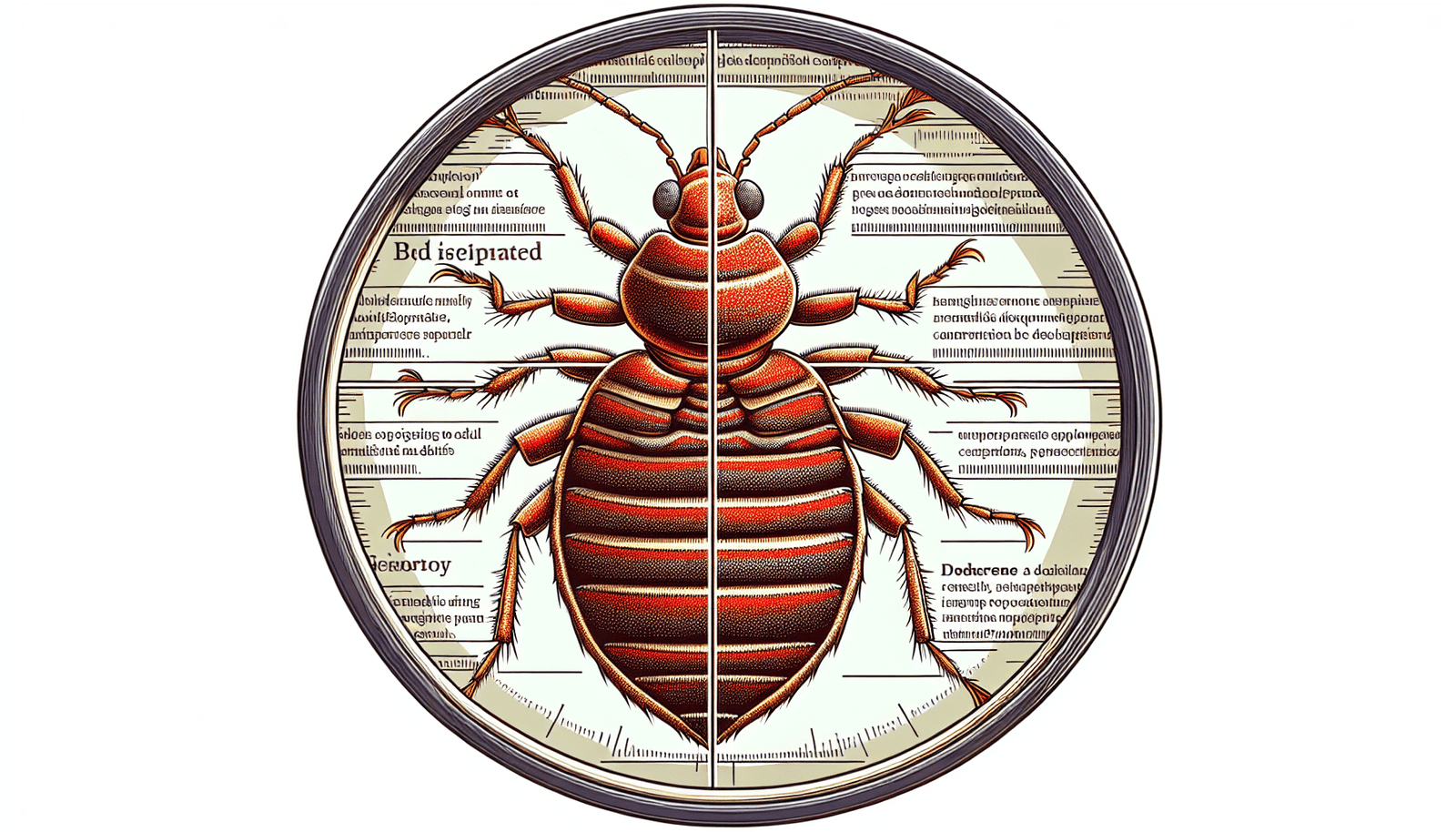
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are small parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are part of the insect order Hemiptera and the family Cimicidae. Bed bugs are wingless and have a flat, oval-shaped body, with a reddish-brown color, although their appearance can vary depending on their age and whether they have recently fed. These nocturnal pests belong to the same family as kissing bugs and bat bugs.
Scientific Classification of Bed Bugs
The scientific classification of bed bugs is as follows:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Family: Cimicidae
- Genus: Cimex
- Species: Cimex lectularius
General Physical Description
Adult bed bugs typically measure about 5-7 millimeters in length, which is roughly the size of an apple seed. They have a flat body, which allows them to hide in tight cracks and crevices. Bed bugs have six legs and two antennae. Their bodies are covered with short, golden hairs, giving them a slightly striped appearance. They have a beak-like proboscis that they use to pierce the skin and extract blood.
When young, bed bugs are smaller and lighter in color, often taking on a translucent or whitish appearance. As they mature and feed, they become darker and more reddish-brown in color. After feeding, their bodies become engorged and swell up, making them appear even larger.
Lifespan and Reproduction Cycle
Bed bugs have a relatively short lifespan, with adult females typically living up to one year, while males may only live for a few months. Bed bugs reproduce through a process called traumatic insemination, in which the male pierces the female’s abdomen and inseminates her directly, rather than through the conventional method of copulation.
After mating, female bed bugs lay tiny, white eggs, which are roughly the size of a pinhead. These eggs are usually deposited in clusters or in small cracks and crevices, close to potential hosts. A female bed bug can lay between one to five eggs per day, and in her lifetime, she can produce hundreds of eggs.
The eggs hatch within one to two weeks, and the newly hatched nymphs go through five molts before reaching adulthood. Each nymph stage requires a blood meal to grow, and they can complete their development in as little as a month under ideal conditions. The entire life cycle of bed bugs, from hatching to adulthood, usually takes around four to five weeks.
Where do Bed Bugs Come From?
The History and Origin of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs have been plaguing humans for centuries. Their exact origin is uncertain, but historians believe that bed bugs have been parasitizing humans since ancient times. Archaeological evidence suggests that bed bugs were present in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
Bed bugs were prevalent throughout much of human history, but their populations dramatically declined during the mid-20th century due to the widespread use of insecticides such as DDT. However, in recent decades, there has been a resurgence of bed bug infestations globally, with increased international travel and the development of pesticide resistance being contributing factors.
Global Distribution Patterns
Bed bugs are found all over the world, as they are highly adaptable and can survive in a wide range of environments. They infest both residential and commercial spaces, including hotels, apartments, dormitories, and hospitals. Bed bugs can thrive in both clean and dirty environments, as they are primarily attracted to the presence of human hosts rather than the cleanliness of the surroundings.
In recent years, cities such as New York, London, and Toronto have experienced significant bed bug infestations. However, bed bugs are not limited to urban areas and can be found in rural regions as well. Their distribution is influenced by factors such as population density, travel patterns, and the availability of suitable hiding places.
Where do Bed Bugs Live?
Home Infestations
Bed bugs are primarily indoor pests and are commonly found in bedrooms, particularly in and around the bed. They prefer to hide in close proximity to their hosts to easily access a blood meal during the night. Common hiding spots include mattress seams, box springs, bed frames, headboards, and nearby furniture.
In severe infestations, bed bugs can also be found in other areas of the home, such as cracks in walls, baseboards, electrical outlets, and behind wallpaper. They can even infest upholstered furniture, curtains, and clothing. Bed bugs are expert hitchhikers and can be unknowingly transported from infested locations to new areas through luggage, clothing, and furniture.
Ideas for Preventing Infestations
Preventing bed bug infestations requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
-
Inspect Second-Hand Furniture: Before bringing used furniture into your home, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of bed bugs, such as live bugs, shed exoskeletons, or dark spots of fecal matter.
-
Be Cautious When Traveling: When staying in hotels or other accommodations, inspect the room for signs of bed bugs. Keep your luggage elevated off the floor and away from the bed. Upon returning home, unpack your luggage outside and wash and dry all clothing on high heat.
-
Seal Entry Points: Seal cracks and crevices in walls, baseboards, and electrical outlets to minimize hiding places for bed bugs.
-
Encase Mattresses and Box Springs: Use bed bug-proof encasements to cover your mattresses and box springs, as these can effectively prevent bed bugs from infesting these areas.
-
Regular Cleaning and Decluttering: Regularly vacuum your home, paying extra attention to areas near the bed. Reduce clutter and remove any potential hiding places for bed bugs.
Unique Hiding Places of Bed Bugs
While bed bugs are commonly associated with mattresses and furniture, they are also known to hide in unexpected places. Here are some unique hiding spots where bed bugs may take refuge:
-
Electronics: Bed bugs can crawl into cracks of electronic devices such as laptops, alarm clocks, and even televisions, seeking warm hiding spots.
-
Books and Magazines: Bed bugs can easily slip between the pages of books or magazines, making them unsuspecting carriers of these pests.
-
Picture Frames: The small gaps and crevices behind picture frames provide suitable hiding places for bed bugs.
-
Wallpaper and Wall Hangings: Bed bugs can find harborage behind wallpaper or wall hangings, especially if they have a textured surface.
-
Luggage and Bags: Bed bugs can hide in the pockets, seams, and folds of luggage and bags, making them easy to transport from one location to another.

How do Bed Bugs Feed?
Their Feeding Habits
Bed bugs are nocturnal insects that feed on the blood of humans primarily during the night. They are attracted to the carbon dioxide and warmth emitted by their hosts, allowing them to locate their next meal. Bed bugs have specialized mouthparts that enable them to pierce the skin and extract blood.
When a bed bug feeds, it injects saliva that contains substances that prevent blood clotting and numb the skin, allowing it to feed undisturbed. The feeding process typically takes around 5-10 minutes, during which the bug engorges itself with blood. After feeding, it returns to its hiding place to digest and process the blood meal.
Symptoms of a Bed Bug Bite
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, itchy welts on the skin. However, the degree of reaction can vary from person to person. Some individuals may have no reaction at all, while others may experience intense itching and swelling.
The bites often occur in a linear or clustered pattern, as multiple bugs may feed on the same area of skin. The itching sensation can persist for several days or even weeks, and in some cases, scratching the bites excessively can lead to secondary skin infections.
It is worth noting that bed bug bites are not a reliable indicator of an infestation, as some people may not exhibit any visible signs of being bitten. Additionally, the appearance of bed bug bites can be mistaken for other insect bites or skin conditions, so it is essential to consider other evidence when diagnosing an infestation.
What are the Health Implications of Bed Bug Bites?
Physical Health Impacts
While bed bugs are generally not considered to be carriers of diseases, their bites can cause several physical health implications. The primary health concern associated with bed bug bites is the potential for secondary skin infections. When individuals scratch their bites excessively, they may break the skin, allowing bacteria to enter and cause infection. In severe cases, these infections may require medical attention and antibiotics.
Additionally, repeated exposure to bed bug bites can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. These reactions can range from mild itching and swelling to more severe symptoms such as hives or difficulty breathing. If you experience severe allergic reactions to bed bug bites, seek medical attention promptly.
Mental Health and Psychological Effects
Bed bug infestations can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and well-being. The constant stress and anxiety associated with living in an infested environment can lead to insomnia, anxiety disorders, and even depression. The fear of being bitten during sleep can cause individuals to develop sleep disturbances and paranoia.
Furthermore, the social stigma associated with bed bugs can lead to feelings of shame and embarrassment, causing affected individuals to isolate themselves from friends and family. The psychological toll of dealing with a bed bug infestation should not be underestimated, and seeking support from professionals or support groups may be beneficial for affected individuals.
How to Diagnose a Bed Bug Bite
Difference Between Bed Bug Bites and Other Insect Bites
differentiating bed bug bites from other insect bites or skin conditions can be challenging, as the appearance and reaction vary among individuals. However, there are some distinguishing factors to consider:
-
Bite Pattern: Bed bug bites often appear in a linear or clustered pattern, reflecting the feeding habits of multiple bugs in one area. Other insects may leave random bite marks.
-
Timing and Referring Symptoms: Bed bug bites typically become more noticeable several hours or days after being bitten. They may be accompanied by itching and mild swelling. Other insect bites may cause immediate reactions or show different symptoms.
-
Location: Bed bug bites are commonly found on exposed areas of the body during sleep, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. Other insect bites may occur in different patterns and locations.
It is important to note that even medical professionals may have difficulty distinguishing between insect bites, so professional diagnosis should not solely rely on bite appearance.
Medical Tests and Consultations
If you suspect bed bug bites or an infestation, it is advisable to consult a medical professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. They may perform a physical examination, take a detailed medical history, and evaluate the symptoms to determine the cause of the bites. In some cases, they may recommend additional tests, such as blood tests or skin swabs, to rule out other possible causes.
How to Treat Bed Bug Bites
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Most bed bug bites can be treated with over-the-counter remedies to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Here are some common treatment options:
-
Topical Steroid Creams or Ointments: Applying an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream or ointment can help reduce inflammation, itching, and redness caused by bed bug bites.
-
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can provide relief from allergic reactions and help alleviate itching.
-
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the bites can help reduce swelling and provide temporary relief from itching.
-
Calamine Lotion: Applying calamine lotion to the affected area can provide soothing relief for itching and irritation.
It is essential to carefully follow the instructions on the product packaging and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms worsen or persist.
When to Seek Medical Attention
In some cases, bed bug bites may require medical attention. Seek medical care if:
- The bites are accompanied by severe allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
- The bites develop signs of infection, such as increasing redness, warmth, tenderness, or oozing pus.
- The itching and discomfort are disrupting your sleep or daily activities.
- Home remedies and over-the-counter treatments are not providing adequate relief.
A medical professional can assess the severity of the bites, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide necessary medical care if complications arise.
How to Eliminate Bed Bug Infestations
Do-It-Yourself Techniques
While it can be challenging to completely eradicate a bed bug infestation without professional help, there are some do-it-yourself techniques you can employ to reduce their numbers and prevent their spread:
-
Thorough Cleaning and Vacuuming: Regularly vacuuming your home, including mattresses, furniture, baseboards, and cracks, can help remove bed bugs and their eggs. After vacuuming, promptly dispose of the vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag outside your home to prevent reinfestation.
-
Hot Water Laundering and Drying: Wash and dry infested clothing, bedding, and linens on high heat cycles to kill any bed bugs or eggs.
-
Encasements and Traps: Encasing mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers can trap any existing bugs and prevent them from escaping or feeding. Additionally, using sticky traps or interceptors under bed legs can catch and monitor bed bug activity.
-
Steam Treatment: Using a steamer to treat infested areas, such as cracks, crevices, and furniture seams, can effectively kill bed bugs and their eggs by exposing them to high temperatures.
-
Diatomaceous Earth: Applying food-grade diatomaceous earth in cracks and crevices can dehydrate and kill bed bugs. However, it is crucial to use caution and follow safety guidelines when handling this substance.
Professional Pest Control Services
For severe or persistent bed bug infestations, it is recommended to consult a professional pest control company with experience in bed bug extermination. These professionals utilize various methods, such as chemical treatments, heat treatments, or a combination of both, to effectively eliminate bed bugs from your home.
Professional pest control services can offer tailored solutions based on the extent of the infestation, your specific needs, and the structural characteristics of your residence. They may also provide guidance on preparation steps and post-treatment measures to prevent reinfestation.
Long-Term Strategies to Keep Your House Bug-Free
After successfully eliminating a bed bug infestation, it is essential to implement long-term strategies to prevent their return. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
-
Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of your home to identify any potential signs of bed bugs or other pests. Vigilance and early detection can help prevent infestations from becoming extensive.
-
Proper Bedding Care: Use bed bug-proof encasements on mattresses and box springs to prevent future infestations. Regularly launder bedding, linens, and clothing on high heat cycles, especially after traveling.
-
Sealing Entry Points: Seal cracks, crevices, and other openings in walls, floors, and furniture to minimize hiding places for bed bugs.
-
Travel Precautions: When traveling, thoroughly inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs before unpacking. Keep your luggage elevated off the floor and away from the bed. Upon returning home, unpack luggage outside and wash and dry all clothing on high heat.
-
Education and Awareness: Stay informed about bed bug prevention techniques and signs of infestation. Educate family members, roommates, and guests to be proactive in preventing the introduction and spread of bed bugs.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of future bed bug infestations and ensure a bug-free living environment.
Facts and Myths about Bed Bugs
Common Misunderstandings and Misconceptions
-
Myth: Bed bugs are only found in dirty or unsanitary environments. Fact: Bed bugs can be found in both clean and dirty environments. They are primarily attracted to the presence of human hosts rather than the cleanliness of the surroundings.
-
Myth: Bed bugs are too small to see with the naked eye. Fact: While bed bugs are small, they are visible to the naked eye. Adult bed bugs measure about 5-7 millimeters in length.
-
Myth: Bed bugs only infest beds. Fact: While bed bugs are commonly found in and around beds, they can infest other areas of the home, including furniture, cracks in walls, and electrical outlets.
-
Myth: Bed bugs transmit diseases. Fact: Bed bugs are not known to carry or transmit diseases, although their bites can cause secondary skin infections.
Fact-checking and Clarifying Misinformation
With the rise of misinformation on the internet, it is important to fact-check and clarify certain claims made about bed bugs. Some common misconceptions include:
-
Claim: Essential oils can effectively repel and kill bed bugs. Reality: While some essential oils may have insect-repellent properties, there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness against bed bugs. Professional treatment methods are typically required to eliminate an infestation.
-
Claim: Ultrasonic devices can eliminate bed bugs. Reality: Ultrasonic devices marketed as bed bug repellents have not been scientifically proven to be effective in eliminating bed bug infestations. These devices should not be relied upon as the sole method of control.
-
Claim: Bed bugs are primarily a problem in low-income areas. Reality: Bed bug infestations can occur in all types of environments, regardless of income level. They can affect residential homes, hotels, dormitories, and even upscale establishments.
It is important to rely on credible sources and consult professionals for accurate information on bed bugs and their control.
Preventative Measures Against Bed Bugs
Travel Tips to Avoid Bringing Bed Bugs Home
When traveling, it is crucial to take precautions to avoid bringing bed bugs home with you. Follow these tips to minimize the risk of infestations:
-
Inspect the Room: Thoroughly inspect the hotel room or accommodation for any signs of bed bugs, including live bugs, shed skins, and dark spots on the mattress and furniture.
-
Elevate Luggage: Keep your luggage elevated off the floor and away from the bed or furniture. Consider using luggage stands or placing your luggage in the bathroom, which is less likely to have bed bugs.
-
Pack Bed Bug-proof Encasements: Bring portable bed bug-proof encasements for your luggage and bags. These encasements can help prevent bed bugs from hitchhiking and infesting your belongings.
-
Wash and Dry Clothes: Upon returning home, promptly wash and dry all clothing on high heat cycles. Heat is lethal to bed bugs and can kill any potential hitchhikers.
Routine Household Care to Prevent Infestations
Taking proactive measures in your household can help prevent bed bug infestations. Here are some routine care tips:
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of your home, paying close attention to areas where bed bugs commonly hide, such as beds, furniture, baseboards, and cracks in walls.
-
Reduced Clutter: Minimize clutter in your home, as it provides additional hiding places for bed bugs. Keep your living space clean and tidy.
-
Seal Entry Points: Seal cracks and gaps in walls, floors, and furniture to limit potential hiding spots for bed bugs.
-
Consider Professional Pest Control: Regularly consult with professional pest control services to implement preventive measures and monitor your home for any signs of bed bug activity.
By implementing these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bringing bed bugs into your home and minimize the chances of a full-blown infestation.
In conclusion, bed bugs are pesky insects that can cause physical discomfort and psychological distress. Knowing how to identify, prevent, and treat bed bug bites and infestations is crucial for maintaining a healthy living environment. By implementing preventive measures and seeking professional help when needed, you can effectively manage and control bed bugs in your home. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to preventing extensive infestations. Stay vigilant, educate yourself and others, and take the necessary steps to keep your surroundings bug-free.