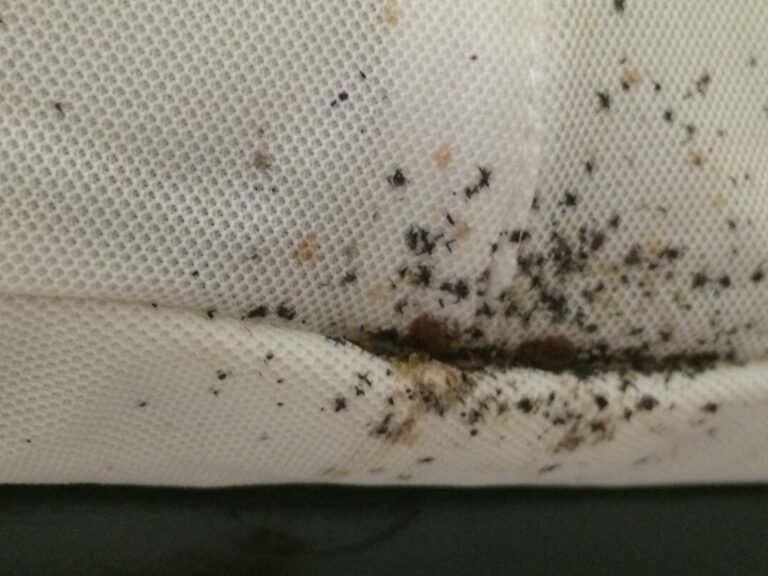
Understanding the Behaviors of Bed Bugs
Understanding the behaviors of bed bugs is crucial in order to effectively deal with them. These tiny insects have become a growing problem in recent years, infesting homes, hotels, and other living spaces. In this article, you will gain insights into the habits and behaviors of bed bugs, enabling you to identify the signs of an infestation and take appropriate measures to eradicate them. From their nocturnal feeding patterns to their ability to hide in various locations, you will learn about the unique characteristics of bed bugs and how to prevent their presence in your environment. Whether you are a homeowner, a traveler, or a pest control professional, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to tackle the challenges posed by bed bugs effectively.
Identifying Bed Bugs
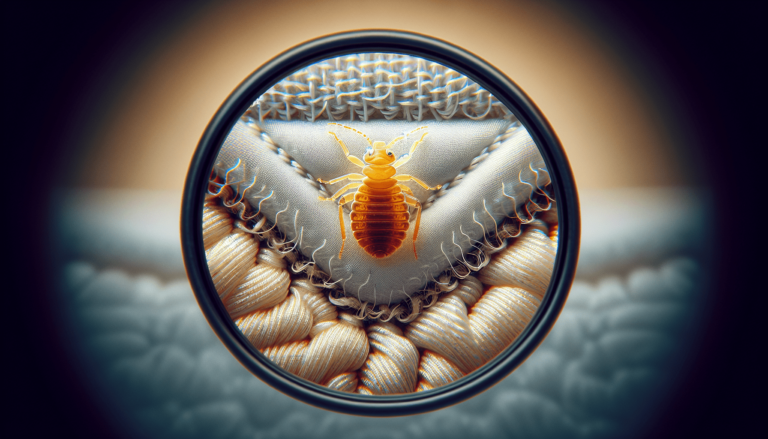
Bed bugs are small, oval-shaped insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. They are nocturnal pests that feed on the blood of humans and animals. Identifying bed bugs can be challenging due to their small size, but there are a few physical characteristics that can help differentiate them from other insects.
Physical characteristics of bed bugs
Bed bugs are approximately the size of an apple seed, ranging from 4 to 5 millimeters in length. They have a flat, oval-shaped body when unfed, but after a blood meal, they become engorged and appear reddish-brown in color. Their bodies are covered in microscopic hairs, giving them a slightly velvety appearance. Bed bugs have six legs and two antennae, which they use to navigate and locate their prey.
Life cycle of bed bugs
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is essential in identifying and controlling infestations. Bed bugs undergo incomplete metamorphosis, meaning they have three distinct life stages: egg, nymph, and adult.
Female bed bugs lay tiny, white eggs, usually in cracks and crevices near a potential food source. These eggs hatch within 6 to 10 days, and the newly emerged nymphs require a blood meal to molt and grow. Nymphs resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs but are lighter in color and translucent. They molt several times before reaching adulthood, and each molt requires a blood meal. The entire life cycle of a bed bug, from egg to adult, can take anywhere from 4 to 9 weeks, depending on environmental conditions and access to a food source.
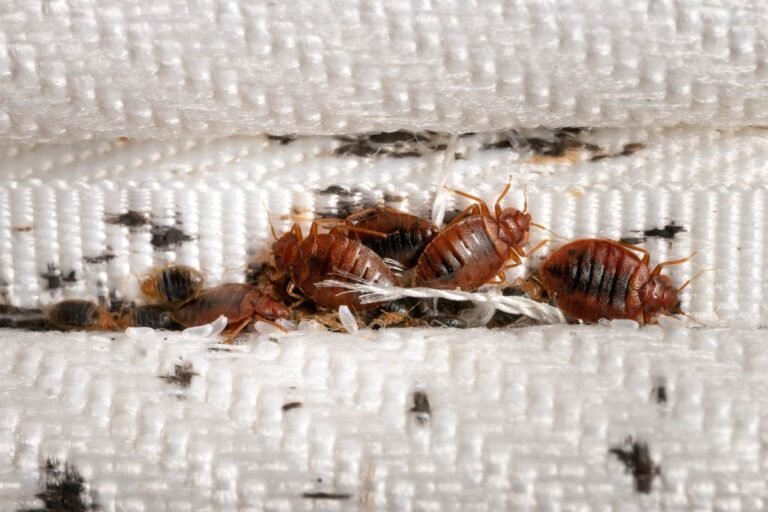
Common habitats
Bed bugs are masters of hiding and can be found in various locations within infested environments. They prefer to reside close to their hosts, usually within 5 to 20 feet of the sleeping area. Common hiding places include mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, and nearby cracks or crevices. However, bed bugs can also infest other items such as furniture, clothing, luggage, and even electrical outlets. Their ability to hitch a ride and survive in various environments contributes to their widespread infestation rates.
Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites are one of the primary indicators of an infestation. While they do not transmit diseases, their bites can cause discomfort and lead to various symptoms in individuals.
Symptoms of bed bug bites
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, itchy welts on the skin. They are often arranged in a linear or clustered pattern, as bed bugs tend to feed in multiple locations during a single feeding session. The severity of the reaction to bed bug bites varies among individuals, with some experiencing mild itching and others developing more severe allergic reactions.
Treatment options for bed bug bites
If you suspect bed bug bites, it is essential to resist the urge to scratch them, as this can lead to skin infections. Instead, focus on relieving the itching and reducing inflammation. Over-the-counter creams containing hydrocortisone can provide temporary relief, and oral antihistamines can help alleviate itching and reduce swelling. If the bites become infected or persist, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further treatment options.
Allergic reactions and complications
While rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to bed bug bites. These reactions can range from mild to severe and may include symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat. In such cases, immediate medical attention should be sought.

Activity Patterns of Bed Bugs
Understanding the activity patterns of bed bugs is crucial for effective control measures. Bed bugs exhibit specific behaviors when it comes to feeding and survival.
Feeding habits
Bed bugs are obligate blood feeders, meaning they rely on blood for their survival and reproduction. They are attracted to the carbon dioxide and warmth emitted by their hosts and usually feed during the night when the host is asleep. They pierce the skin with their sharp mouthparts and inject saliva that contains anticoagulants to prevent blood clotting. Bed bugs usually feed for about 5 to 10 minutes before retreating to their hiding spots.
Nocturnal behavior
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal creatures, with their peak activity occurring during the night. They are attracted to the darkness and the warmth of their hosts. However, in heavily infested environments or when hungry, they may become bolder and feed during the daytime as well. Their nocturnal behavior makes it challenging to detect infestations, as they can remain hidden during the day.
Survival and hibernation patterns
Bed bugs are highly resilient and can survive for extensive periods without a blood meal. Depending on environmental conditions, they can live for several months to a year or more without feeding. However, they are unable to enter true hibernation and can remain active even in colder temperatures, although their activity may slow down.
Bed Bug Infestation Indicators
Identifying the signs of a bed bug infestation is essential for prompt intervention and control. Early detection can prevent infestations from spreading and becoming more challenging to eliminate.
Signs of bed bugs
One of the most obvious signs of a bed bug infestation is the presence of live bugs. These bugs can be found in their hiding places, such as mattresses, furniture, or cracks and crevices near the bed. They are often visible to the naked eye, especially in severe infestations.
Presence of bed bug shells and feces
Bed bugs shed their exoskeletons as they grow, leaving behind empty shells. These exoskeletons, known as molted skins, can be found near their hiding spots or in areas where they feed. Additionally, bed bugs leave behind dark, rust-colored fecal stains on sheets, mattresses, and other surfaces they infest. These stains may resemble small specks or smears and are a result of the digested blood that they excrete.
Unexplained bites and rashes
Waking up with unexplained bites or rashes that appear in clusters or linear patterns is a strong indicator of a bed bug infestation. These bites can be itchy and cause considerable discomfort. If multiple individuals living in the same household experience similar symptoms, it is crucial to investigate for a potential bed bug infestation.

Reproduction and Growth of Bed Bugs
Understanding the reproductive capabilities and growth stages of bed bugs aids in developing effective control strategies. Bed bugs are prolific breeders, and a single infestation can quickly escalate if left unchecked.
Bed bug mating process
Bed bugs reproduce through a process called traumatic insemination. During this process, the male bed bug pierces the female’s abdomen with his reproductive organ, injecting sperm directly into her body cavity. This method of mating can lead to physical damage and potential infections in female bed bugs.
Egg laying and hatching
After mating, female bed bugs lay their eggs in discreet locations near potential food sources, such as cracks, crevices, and upholstery. A female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs throughout her lifetime. These eggs are tiny, whitish in color, and approximately 1 millimeter in length. They are often cemented to surfaces and are difficult to spot without close inspection. The eggs hatch within a week to ten days, giving rise to nymphs.
Growth stages
Nymphs, the immature stages of bed bugs, emerge from the eggs and undergo multiple molts to reach adulthood. Each nymph stage requires a blood meal to molt and grow. Nymphs resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs but are lighter in color and translucent. They become darker and more distinguishable as they feed and molt. The time it takes for nymphs to reach adulthood varies depending on various factors, such as temperature, availability of food, and surrounding conditions.
Bed Bug Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling bed bug infestations require a multi-pronged approach that addresses their hiding spots and disrupts their ability to feed and reproduce.
Regular cleanliness and hygiene
Maintaining cleanliness and hygiene in living spaces can help prevent bed bug infestations. Regularly vacuuming mattresses, upholstered furniture, and other potential hiding spots can remove bed bugs and their eggs. Washing bedding, linens, and clothing in hot water and drying them on high heat can also help eliminate any bed bugs present.
Professional pest control services
In severe infestations or cases where self-treatment has proven ineffective, it is advisable to seek the assistance of professional pest control services. Pest control professionals are trained to identify and effectively eliminate bed bug infestations using a combination of chemical treatments, heat treatments, and targeted applications.
Use of bed bug repellents and chemicals
Certain bed bug repellents and insecticides can be used as a preventative measure to deter bed bugs from infesting specific areas. These products typically contain specific chemicals that are toxic to bed bugs, disrupting their nervous system and leading to their eventual death. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and exercise caution while using these products, especially in areas where children and pets may come into contact.
Effects of Bed Bugs on Human Health
Bed bugs not only cause physical discomfort but can also have psychological and health-related consequences for those affected by infestations.
Psychological impact of bed bugs
Bed bug infestations can have a significant psychological impact on individuals and families. The fear and anxiety surrounding the presence of these pests can lead to sleep disturbances, paranoia, and feelings of shame or embarrassment. The constant itching from bed bug bites can also disrupt daily activities and contribute to increased stress levels.
Physical health risks
Although bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can lead to secondary complications. Scratching the bites can cause breaks in the skin, making individuals more susceptible to bacterial infections. Additionally, frequent exposure to bed bug bites can lead to anemia in severe cases, particularly in individuals who are already anemic or have weakened immune systems.
Preventing skin infections
To reduce the risk of skin infections, it is important to avoid scratching bed bug bites. Applying over-the-counter antiseptic creams or ointments to the affected areas can help prevent bacterial infections. Keeping the bites clean and dry and avoiding further irritation can aid in the healing process.
Misconceptions about Bed Bugs
There are several misconceptions surrounding bed bugs that can hinder effective prevention and control efforts. Understanding these misconceptions can help individuals make informed decisions when dealing with potential infestations.
Bed bugs and cleanliness
Contrary to popular belief, bed bugs are not solely attracted to dirty or unsanitary environments. They can infest even the cleanest of spaces as long as there is a source of blood nearby. Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can be transported from infested areas to clean spaces via clothing, luggage, or furniture.
Bed bugs transmission of diseases
While bed bugs are known to feed on humans and animals, they are not known vectors for transmitting diseases. Extensive research has shown no evidence of bed bugs transmitting infectious agents or pathogens through their bites. However, their presence and the resulting psychological and physical impacts can still cause significant distress and discomfort.
Bed bugs and property type
Bed bugs can infest any type of property, regardless of its cleanliness or socioeconomic status. They do not discriminate and can be found in both residential and commercial environments. Hotels, apartments, dormitories, hospitals, and even public transportation have been known to experience bed bug infestations. Vigilance, early detection, and proper prevention methods are key to reducing the risk of infestation.
Global Spread and Travel Habits of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs have become a global issue, with increased travel and global transportation contributing to their rapid spread across different countries and continents.
Travel patterns of bed bugs
Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily be transported from one location to another through human activities. Infested luggage, clothing, and furniture are common vehicles for introducing bed bugs into previously unaffected areas. Traveling, whether domestically or internationally, increases the risk of encountering bed bugs and inadvertently bringing them back to one’s living space.
Rise in global bed bug infestations
Over the past few decades, bed bug infestations have seen a significant resurgence worldwide. The reasons for this increase are multifaceted, including changes in pest control practices, increased resistance to insecticides, and a lack of public awareness about prevention methods. The rise in global travel has also played a crucial role in the spread of bed bugs, as they can easily hitch a ride on luggage and personal belongings.
Impact of travel and transportation on the spread of bed bugs
The interconnectedness of the modern world through travel and transportation has facilitated the rapid spread of bed bugs. Infestations can occur in hotels, airplanes, trains, and other forms of public transportation, creating opportunities for bed bugs to find new hosts and establish populations in different areas. Vigilance when traveling and taking preventive measures, such as inspecting accommodations and luggage, can help minimize the risk of encountering bed bugs and bringing them back home.
Scientific and Research Findings on Bed Bugs
Ongoing research and scientific studies provide valuable insights into the behavior, biology, and control methods of bed bugs. These findings contribute to the development of effective strategies for managing infestations.
Latest research on bed bug behavior
Scientists continue to study various aspects of bed bug behavior, including their feeding preferences, mating habits, and resistance to insecticides. This research helps in understanding the biology and ecology of bed bugs, enabling the development of targeted control methods.
Development of new treatment methods
The emergence of insecticide resistance in bed bugs has prompted researchers to explore alternative treatment options. Studies are underway to evaluate the efficacy of non-chemical approaches, such as heat treatments, steam, freezing, and biological controls, in managing bed bug infestations. These innovative methods offer potential solutions for areas where traditional insecticides have proven less effective.
Scientifically-proven prevention methods
Research has also shed light on effective prevention methods for bed bugs. Studies have shown the importance of early detection and prompt intervention to prevent infestations from becoming widespread. Regular inspections, proper sanitation practices, and the use of bed bug-proof encasements for mattresses and box springs have been shown to be effective in minimizing the risk of infestations.
In conclusion, understanding the behaviors of bed bugs is crucial for identifying, preventing, and controlling infestations. By recognizing the physical characteristics, activity patterns, and reproductive traits of bed bugs, individuals can take appropriate measures to mitigate the risks associated with these pests. Additionally, staying informed about the global spread of bed bugs and the latest scientific findings can contribute to more effective management strategies. Remember to seek professional assistance when necessary, and prioritize cleanliness and hygiene to minimize the chances of encountering bed bugs.