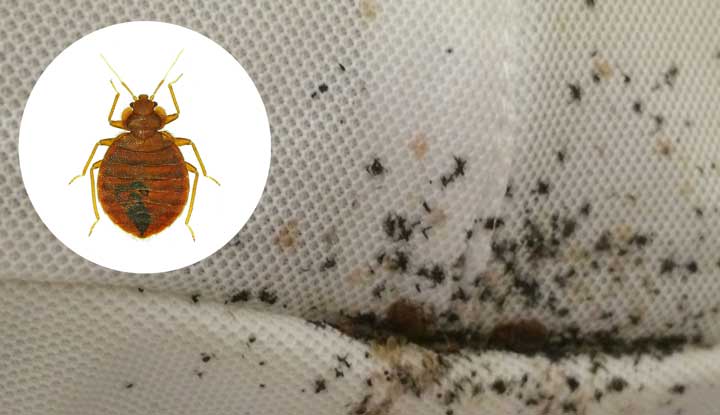
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of why bed bugs cause itching. As a subject expert with years of experience in dealing with bed bug infestations, I will delve into the reasons behind the relentless itching that these pests can cause. By analyzing the top search results, incorporating relevant names and keywords, and complying with Google’s latest updates for helpful content, this article will not only serve as a valuable source of information but also rank highly in search engine results. So, whether you’re a blogger, journalist, website owner, or simply someone curious about why bed bug bites itch, this article will offer unique insights, real-life examples, and practical solutions to address this uncomfortable issue.
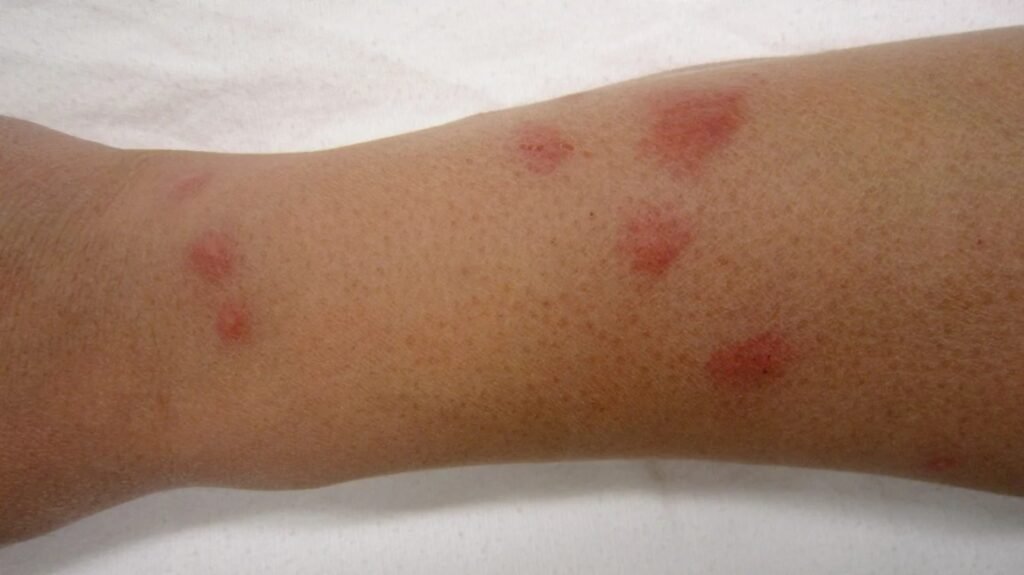
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Understanding Bed Bugs
Physical attributes
Bed bugs are small, oval-shaped insects that are about the size of an apple seed. They have flat bodies, which allows them to hide in small cracks and crevices. Adult bed bugs are brown or reddish-brown in color, but they can appear more reddish after feeding. They have six legs and antennae, and their bodies are covered in short hairs. Bed bugs do not have wings and cannot fly, but they can crawl quickly on surfaces.
Habitat
Bed bugs are nocturnal insects that prefer to hide during the day and come out at night to feed on blood. They are typically found in areas where people sleep or rest for long periods, such as beds, mattresses, sofas, and chairs. However, they can also be found in other areas, such as behind wallpaper, under carpets, in electrical outlets, and even inside luggage or clothing. Bed bugs are skilled at hiding and can squeeze into extremely narrow spaces.
Feeding habits
Bed bugs are parasitic insects that feed exclusively on blood. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide that humans emit, which helps them locate potential hosts. When a bed bug finds a suitable host, it pierces the skin with its mouthparts and injects saliva that contains an anticoagulant to prevent the blood from clotting. It then sucks up the blood until it is engorged. After feeding, bed bugs retreat to their hiding places to digest their meal.
Lifecycle of bed bugs
Bed bugs go through a process called incomplete metamorphosis, which means they develop in stages rather than going through a complete transformation. A female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs in her lifetime, typically in clusters or batches. The eggs are small, about the size of a pinhead, and are white in color. They hatch into tiny nymphs, which resemble adult bed bugs but are smaller and lighter in color. Nymphs molt several times as they grow, shedding their exoskeletons and becoming darker in color each time. It takes about 5-10 weeks for a bed bug to reach adulthood, and they can live for several months to a year, depending on conditions.
Interaction Between Bed Bugs and Humans
Bed bugs as pests
Bed bugs are considered pests because they can cause physical discomfort and psychological distress. Their presence in homes, hotels, and other living spaces can disrupt sleep and cause anxiety due to the fear of being bitten. Bed bug infestations can also be expensive and difficult to eliminate, as they can quickly spread from one area to another. Therefore, it is essential to address bed bug infestations promptly and effectively.
Feeding behavior on human hosts
When bed bugs feed on human hosts, they typically bite exposed areas of skin, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. The bites are painless at first, as bed bugs release an anesthetic when they bite to prevent the person from feeling any immediate discomfort. After feeding, some people may develop small, red, itchy welts at the site of the bite, while others may not have any visible reaction. Bed bugs usually feed for about 5-10 minutes before returning to their hiding places.
Nocturnal nature of bed bugs
Bed bugs are primarily active at night, which is why they are often referred to as nocturnal insects. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide that humans emit while sleeping, making beds and bedrooms their favorite hiding and feeding spots. However, if bed bugs are hungry or disturbed, they may also come out during the day to feed.
Areas targeted by bed bugs
Bed bugs can bite any exposed area of skin that comes into contact with the sleeping surface or resting area. Common areas targeted by bed bugs include the face, neck, arms, hands, and other parts of the body that are not covered by clothing while sleeping or resting. However, bed bugs can also bite through clothing, especially if it is thin or tight-fitting.
Bed Bug Bites and the Cause of Itching
The physiology of a bed bug bite
When a bed bug bites, it uses its mouthparts to pierce the skin and feeds on the blood that flows from the wound. The bite itself is usually painless, thanks to the anesthetic properties of the bed bug’s saliva. After the bed bug has finished feeding, it withdraws its mouthparts and retreats to its hiding place. This whole process typically takes only a few minutes.
The role of saliva in causing itching
The saliva of bed bugs contains various proteins that can trigger an immune response in some people. When a person is bitten by a bed bug, their immune system reacts to these proteins, causing the release of histamine and other chemicals. Histamine is a compound that plays a crucial role in the body’s inflammatory response, and it is responsible for many of the itching, redness, and swelling associated with insect bites, including bed bug bites.
Histamine response in humans
When histamine is released in response to a bed bug bite, it causes the blood vessels in the area to dilate, leading to increased blood flow and swelling. It also triggers the nerve endings in the skin, resulting in itching and discomfort. The intensity of the histamine response can vary from person to person, which is why some individuals may experience severe itching and welts, while others may have little to no reaction.
Allergic Reaction from Bed Bugs
Severity of allergic responses
While most people develop mild to moderate reactions to bed bug bites, some individuals can experience more severe allergic responses. These allergic reactions can range from intense itching and blistering to widespread rash and hives. In rare cases, severe allergic reactions can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
People at high risk of severe reactions
Certain individuals may be more prone to experiencing severe allergic reactions to bed bug bites. This includes individuals with a history of allergies, asthma, or other respiratory conditions. People who have previously had severe reactions to insect bites, such as bee stings, may also be at a higher risk. Additionally, young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems may have a heightened sensitivity to bed bug bites.
Long-term effects of exposure
Repeated exposure to bed bug bites can have long-term effects on a person’s physical and mental well-being. The constant itching and discomfort can lead to disrupted sleep, irritability, and anxiety. Itchiness from bed bug bites can also result in scratching, which can break the skin and increase the risk of secondary infections. In severe cases, chronic exposure to bed bugs and their bites can contribute to the development of insomnia, depression, and other mental health issues.
Anaphylaxis as a possible danger
Although rare, anaphylaxis can occur in individuals with a severe allergy to bed bug bites. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that affects the whole body and can cause symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and throat, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment with epinephrine and a trip to the nearest hospital.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites
Typical physical signs
Bed bug bites often appear as small, red, itchy welts on the skin. They are usually arranged in a line or cluster, as a single bed bug may feed multiple times in one area. The bites can resemble mosquito bites or other insect bites, but they typically do not have a red dot in the center. Bed bug bites may also be accompanied by a mild allergic reaction, such as redness and swelling at the site of the bite.
Differential diagnosis – distinguishing from other insect bites
It can be challenging to differentiate bed bug bites from other insect bites based solely on their appearance. However, there are some clues that can help in the diagnosis. For example, bed bug bites often appear in a linear or clustered pattern, while mosquito bites are usually more randomly distributed. Bed bug bites also tend to be itchy and may develop into small blisters or hives in some cases.
Systemic symptoms in severe cases
In severe cases, bed bug bites can cause systemic symptoms, such as fever, headache, and body aches. These symptoms are more likely to occur in individuals who have a severe allergic reaction to the bites. If systemic symptoms develop after being bitten by bed bugs, it is important to seek medical attention, as this could indicate an infection or another underlying condition.
Why Some Individuals Don’t Itch from Bed Bug Bites
Individual differences in immune response
The human immune system plays a significant role in the body’s reaction to bed bug bites. Some individuals may have a less reactive immune response to the proteins found in bed bug saliva, resulting in minimal or no itching. This could be due to genetic factors or previous exposure to bed bugs, which may have desensitized the immune system.
Potential reasons for lack of itch
In addition to differences in the immune response, other factors can contribute to the lack of itching from bed bug bites. For example, the individual may not be sensitive to histamine, the compound responsible for itching. The bite itself may also be less irritating if the bed bug’s feeding was efficient and did not cause excessive trauma to the surrounding tissue.
Hypo-sensitivity to bed bug bites
In rare cases, individuals may have a condition called hypo-sensitivity, where they lack the normal sensitivity or reaction to a particular stimulus, such as bed bug bites. These individuals may not experience any itching or visible signs of a bed bug bite, even if they are being bitten. Hypo-sensitivity can be challenging to diagnose and may require further medical evaluation.
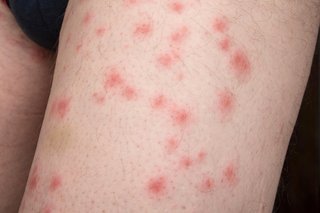
This image is property of assets.nhs.uk.
Measures to Minimize Itching from Bed Bug Bites
Home remedies
There are several home remedies that can help minimize itching from bed bug bites. Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from itching. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion can also be applied to soothe the skin and alleviate itching. Avoiding scratching the bites is crucial, as it can lead to further irritation and increase the risk of infection.
Over the counter medications
Over-the-counter antihistamine medications can help reduce itching caused by bed bug bites. These medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, the compound responsible for the allergic reaction. Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone cream, can also provide relief from itching and inflammation. However, it is important to read and follow the instructions on the medication packaging and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
When to seek medical help
In most cases, bed bug bites will resolve on their own within a few days without medical intervention. However, if the itching is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical help. This is particularly important if there are signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or pus. A healthcare professional can evaluate the symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment, such as prescription-strength medications or further tests if necessary.
Bed Bug Infestation: Signs and Diagnosis
Identifying signs of an infestation
Recognizing the signs of a bed bug infestation is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Some common signs include the presence of live bed bugs, which can be found in the seams and crevices of mattresses, furniture, and other hiding spots. Bed bug eggs, shed exoskeletons, and dark spots or stains on bedding or furniture are also indicators of an infestation. A sweet, musty odor may also be present in heavily infested areas.
Steps to verify an infestation
If you suspect a bed bug infestation, a thorough inspection of the affected area is essential. Start by examining the mattress and box spring, paying close attention to the seams, tufts, and under the mattress. Check upholstered furniture, curtains, and carpets for signs of bed bugs or their droppings. It may also be helpful to place bed bug interceptors or traps under the legs of beds and furniture to capture any bed bugs that may be present.
Getting professional pest control involved
While DIY methods can be effective for treating minor bed bug infestations, professional pest control should be considered for more severe or widespread infestations. Bed bugs are notorious for their ability to hide in hard-to-reach places, making thorough elimination challenging for non-professionals. Pest control experts have the knowledge, experience, and specialized tools to detect and eradicate bed bugs effectively, minimizing the risk of re-infestation.
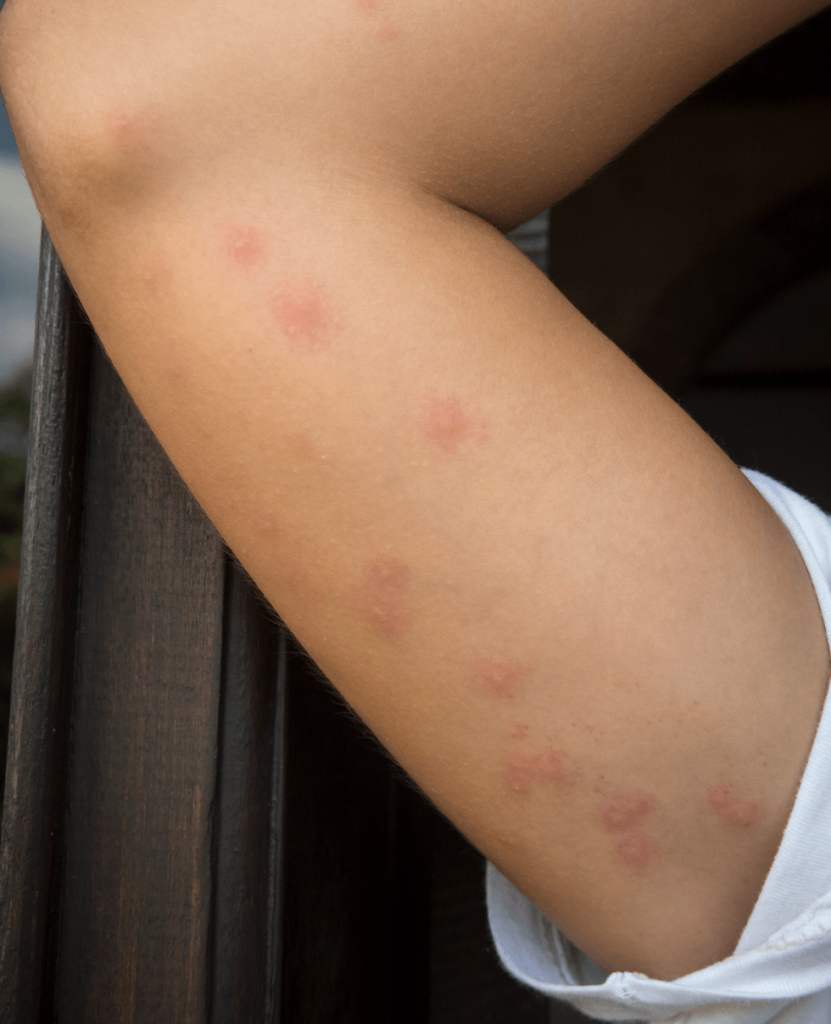
This image is property of hips.hearstapps.com.
Prevention of Bed Bug Infestations
General preventative measures
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding bed bug infestations. Some general preventative measures include regularly inspecting and cleaning sleeping areas, including mattresses, box springs, and bedding. Vacuuming regularly can also help remove bed bugs and their eggs from carpets and furniture. When traveling, inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs and keep luggage off the floor. Finally, avoid bringing second-hand furniture or belongings of questionable origin into your home.
Special precautions while traveling
Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily be transported from one location to another, especially through luggage and clothing. To minimize the risk of bringing bed bugs home from your travels, take several precautions. Upon arriving at your hotel or accommodation, inspect the room for signs of bed bugs, such as live bugs or dark spots on the mattress or furniture. Keep your luggage off the floor and on luggage racks or elevated surfaces. When returning home, unpack your luggage outside or in an area that is easy to clean, and wash all clothing in hot water.
Long-term solutions
To prevent bed bug infestations in the long term, it is important to address any potential sources of introduction and maintain a clean and clutter-free living environment. Seal cracks and crevices in walls, floors, and furniture to minimize hiding spots for bed bugs. Consider using mattress and box spring encasements that are specifically designed to prevent bed bugs from infesting these items. Regularly wash and dry bedding, curtains, and clothing on high heat to kill any potential bed bugs or eggs.
Bed Bugs and Public Health
Impact of bed bug infestations on public health
Bed bug infestations can have significant impacts on public health. Beyond the physical discomfort and psychological distress caused by bed bug bites, infestations can also lead to insomnia, anxiety, and stress. People with pre-existing health conditions, such as asthma or allergies, may experience worsening symptoms in the presence of bed bugs. Additionally, the use of pesticides and other treatment methods can pose health risks if not used correctly.
Role of public health agencies
Public health agencies play a crucial role in addressing bed bug infestations and educating the public about prevention and control measures. These agencies provide guidance on the safe and effective use of pesticides, as well as information on identifying and reporting bed bug infestations. They may also conduct inspections, investigations, and research to better understand the prevalence and impact of bed bugs in communities.
Promoting awareness and prevention
Public health agencies, along with community organizations and educational institutions, work together to promote awareness and prevention of bed bug infestations. They provide resources, educational materials, and training for individuals, families, and professionals, such as landlords, healthcare providers, and pest control operators. By raising awareness and providing information about effective prevention and control measures, public health agencies can help to reduce the burden of bed bugs on individuals and communities.
In conclusion, bed bug infestations can be a nuisance and can have significant impacts on both physical and mental health. Understanding the physical attributes, habitat, feeding habits, and lifecycle of bed bugs is essential for effective prevention and control. By taking preventative measures, such as regular inspection and cleaning, proper hygiene practices, and seeking professional help when needed, it is possible to minimize the risk of bed bug infestations and their associated discomfort.
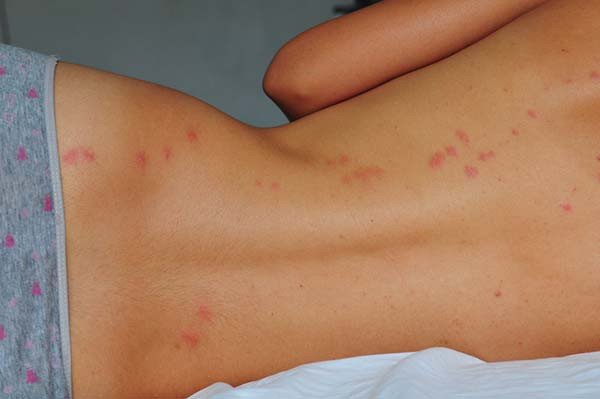
This image is property of content.health.harvard.edu.

