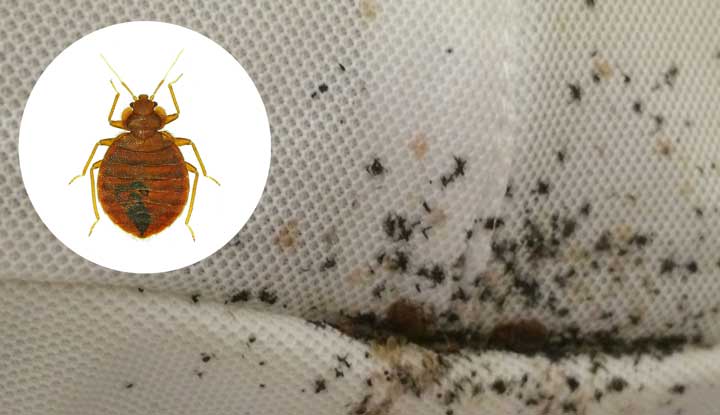
Why do bed bugs bite? Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are parasitic insects that feed exclusively on blood. Despite their name, bed bugs do not exclusively infest beds; they can be found in various locations such as upholstered furniture, cracks in walls, and even clothing. Bed bug bites can cause itchy welts and may lead to allergic reactions in some individuals. Understanding why bed bugs bite is essential in preventing infestations and effectively addressing the problem. In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind bed bug bites, explore their behavior, and provide valuable insights and solutions to deal with these pesky creatures. So, whether you have personally dealt with a bed bug infestation or are simply curious about these bloodsuckers, this article aims to provide the comprehensive information you need.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Understanding Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are small, wingless insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. They are nocturnal pests that feed on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Bed bugs are considered to be one of the most troublesome and persistent pests, causing discomfort and distress to individuals and families. They are efficient hitchhikers and can easily spread from one location to another, making it crucial to understand their behaviors, anatomy, and ways to prevent infestations.
Definition and description of bed bugs
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are flat, oval-shaped insects that are approximately the size of an apple seed when fully grown. They have six legs and are typically reddish-brown in color. These parasites are known for their ability to hide in small cracks and crevices, especially in and around sleeping areas such as beds, mattresses, and upholstery.
Lifespan and reproduction of bed bugs
The lifespan of a bed bug typically ranges from four to six months, during which time they go through several life stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Female bed bugs can lay up to five eggs per day and over 500 eggs during their lifetime. The eggs are tiny, about the size of a pinhead, and are often laid in clusters in hidden areas near their food source. The eggs hatch into nymphs, which are smaller versions of the adults and require a blood meal to molt and grow into the next stage.
Habitats and infestation of bed bugs
Bed bugs are known for their ability to infest both residential and commercial properties, including hotels, hospitals, dormitories, and even public transportation. They can easily hitch a ride on luggage, clothing, or furniture and be transported to new locations. These pests are most commonly found in areas where people sleep, rest, or spend prolonged periods of time, as they are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by humans. It is important to note that bed bugs are not a reflection of poor hygiene or cleanliness, as they can infest even the cleanest of environments.
The Anatomical Structure of Bed Bugs
To effectively control and treat bed bug infestations, it is important to understand the anatomical structure of these pests, including their physical features, mouthparts, and color changes throughout their life stages.
Physical features and size
Adult bed bugs are approximately 5-7 millimeters in length, about the size of an apple seed. They have a flat, oval-shaped body with a hard exoskeleton. Their bodies are segmented and divided into three distinct parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. Bed bugs have six legs, each with tiny claws that enable them to crawl and cling to surfaces.
Mouthparts and functionality
The mouthparts of bed bugs are designed for piercing the skin of their hosts and extracting blood. They possess a long, tubular structure known as a proboscis, which is composed of two stylets. One stylet acts as a hypodermic needle, injecting saliva into the host, while the other acts as a straw, sucking up blood. Bed bugs are able to detect the presence of a suitable host through heat, carbon dioxide, and other chemical cues.
Color and changes through life stages
Bed bugs undergo distinct color changes as they progress through their life stages. Newly hatched bed bugs, or nymphs, are translucent and nearly colorless. As they feed and grow, they become darker in color, eventually turning reddish-brown. After a blood meal, their bodies swell and elongate, making it easier to distinguish them from unfed bed bugs. The coloration of bed bugs can vary depending on factors such as age, feeding status, and the presence of other environmental factors.
Bed Bug Biting Mechanism
Understanding the process of a bed bug bite, as well as the unique characteristics of bed bug bites, can help individuals identify and address infestations promptly.
The process of a bed bug bite
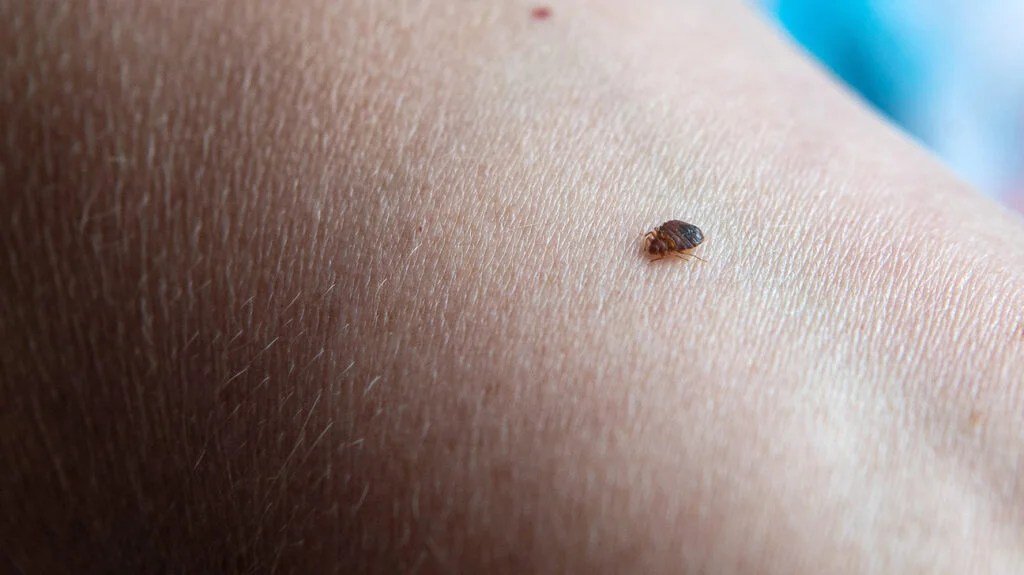
When a bed bug locates a suitable host, it uses its sharp mouthparts to pierce the skin and inject saliva. The saliva contains an anesthetic and anticoagulant, which allows the bed bug to feed without being noticed and to obtain a steady blood flow. Bed bug bites are typically painless and often go unnoticed until after the feeding has occurred.
Unique characteristics of bed bug bites
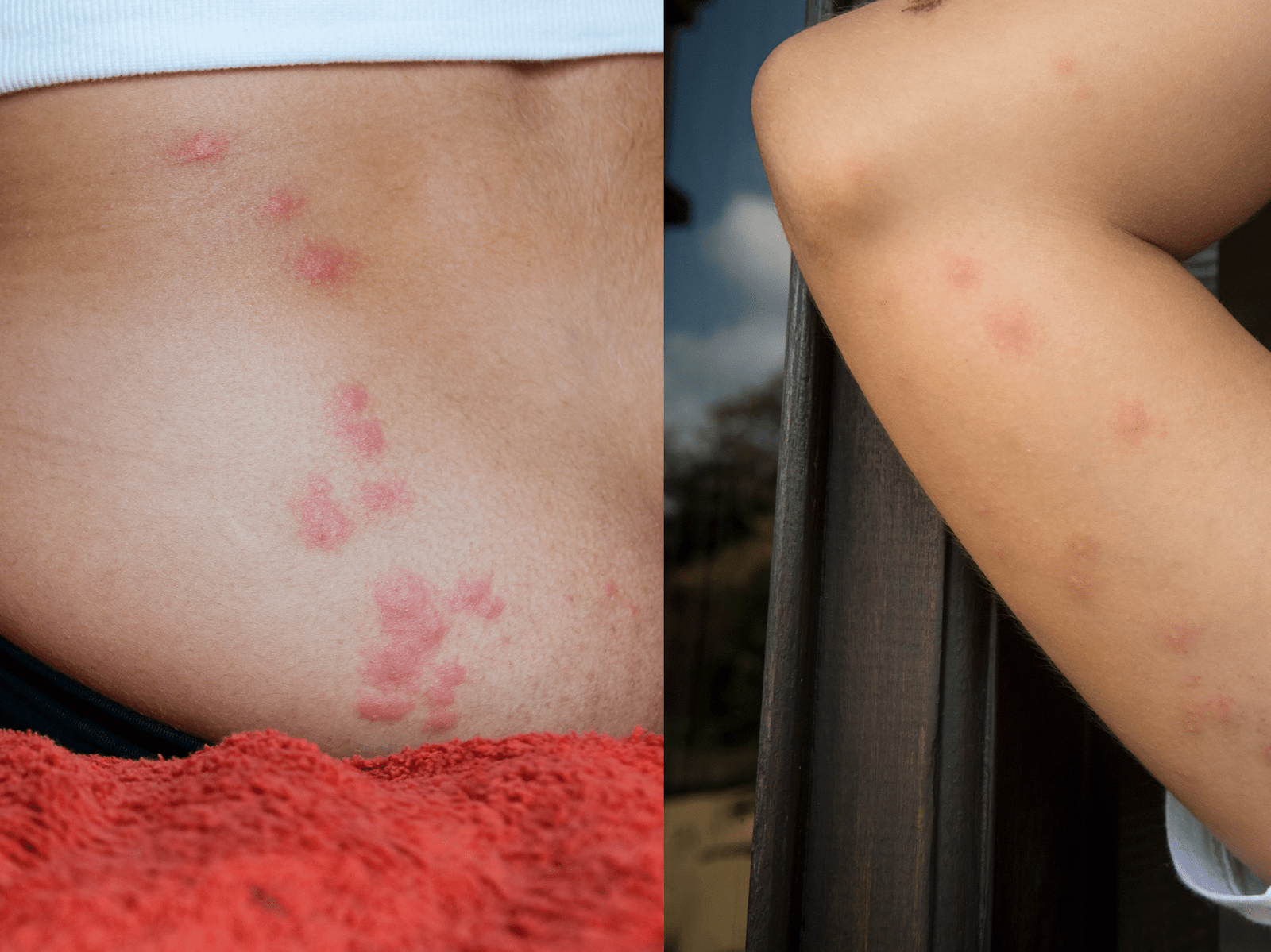
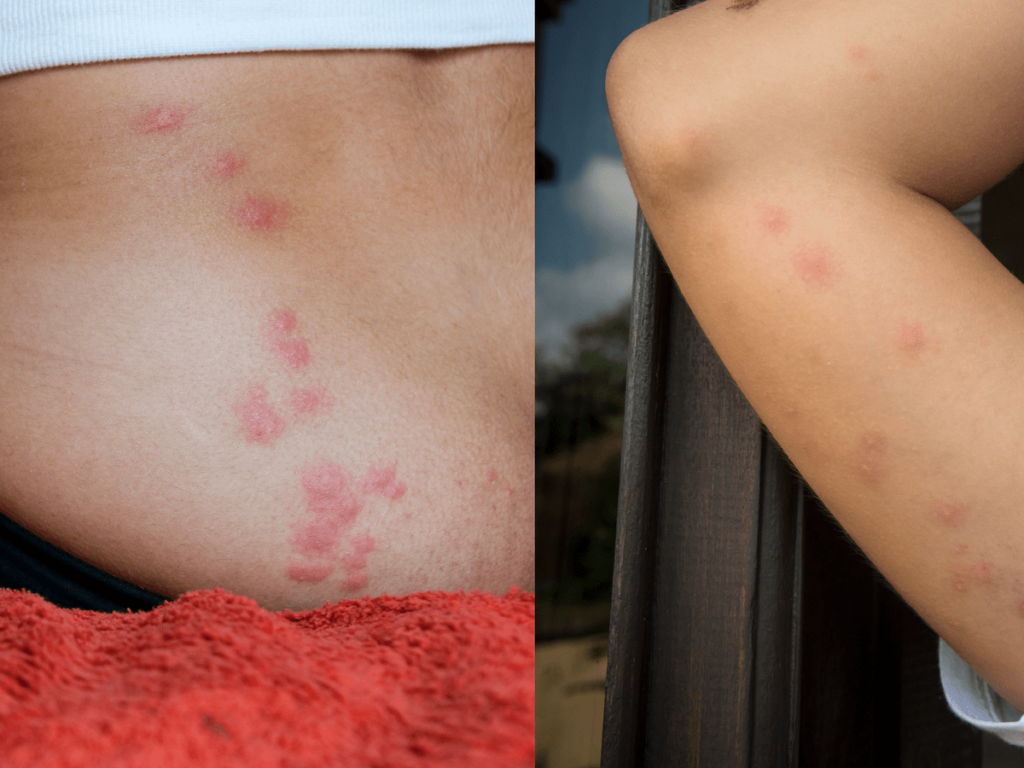
Bed bug bites are characterized by several distinctive features. They often appear in a line or cluster, as bed bugs tend to feed in close proximity to one another. The bites are commonly found on exposed areas of the body, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. bed bug bites can cause itching, redness, and swelling, similar to other insect bites, but individual reactions can vary.
Frequency and timing of bites
Bed bugs are attracted to their hosts by body warmth and carbon dioxide, which are released during sleep. Therefore, most bed bug bites occur during the night while individuals are sleeping. However, in severe infestations or situations where bed bugs have easy access to hosts during the day, bites can occur at any time. The frequency of bites can vary depending on the size of the infestation and the number of available hosts.
Why Bed Bugs Bite Humans
Bed bugs bite humans primarily out of necessity for survival and development. Understanding their motivations can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent infestations and control existing ones.
Necessity for survival and development
Bed bugs rely on blood meals for nourishment and to molt into the next stage of their life cycle. Without regular access to blood, bed bugs are unable to reproduce and complete their life cycle. Therefore, biting humans is crucial for their survival and propagation.
Attraction to body warmth and carbon dioxide
Bed bugs are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by human bodies, which serve as indicators of a suitable blood meal. When individuals are asleep or resting, their body temperature and carbon dioxide levels increase, making them particularly attractive to bed bugs. This is why bed bug bites are commonly found on exposed areas of the body during sleep.
Reload of bed bug digestion and reproduction processes
When bed bugs feed on blood, they are able to reload their digestive system and obtain the necessary nutrients for reproduction. Blood serves as a valuable source of protein and other essential compounds that fuel their growth and development. Without frequent blood meals, bed bugs are unable to sustain their populations.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Effects of Bed Bug Bites on Humans
While bed bug bites are generally not considered dangerous, they can cause physical reactions, psychological distress, and disrupt sleep patterns. Recognizing the effects of bed bug bites can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and take preventive measures.
Physical reactions and symptoms
Bed bug bites often cause redness, swelling, and itching. Some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to the saliva injected by bed bugs, leading to more severe symptoms such as blisters, hives, or even anaphylaxis in rare cases. Excessive scratching of the bites can also lead to secondary infections.
Psychological and sleep effects
The presence of bed bugs and their bites can have significant psychological effects on individuals. The fear and anxiety associated with the presence of these pests can lead to sleep disturbances, insomnia, and emotional distress. Individuals may experience heightened stress and difficulty maintaining a sense of well-being in infested environments.
Risk of disease transmission
While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can result in secondary infections if the skin is broken due to scratching. Scratching bed bug bites can introduce bacteria from the nails or other surfaces into the skin, increasing the risk of infection. Additionally, the psychological impact of infestations can have negative effects on mental health.
How to Recognize a Bed Bug Bite
Being able to recognize a bed bug bite is essential for prompt identification and treatment. Understanding the common signs and symptoms, as well as differentiating bed bug bites from other insect bites, can help individuals take appropriate action.
Common signs and symptoms
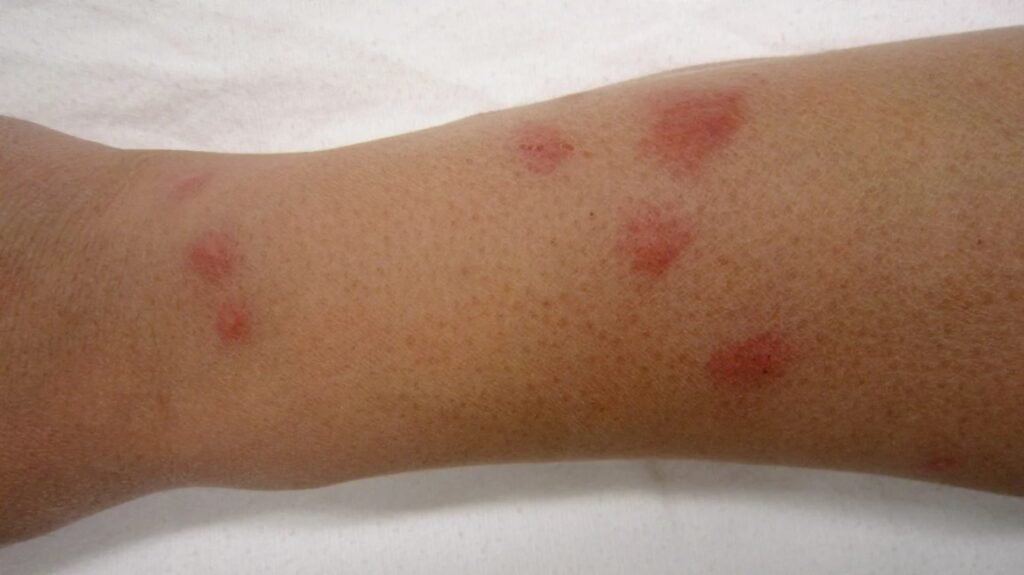
Bed bug bites often present as small, raised welts or bumps on the skin. They can be red, itchy, and occur in clusters or a line. The bites may develop a blister-like appearance in some cases. It is important to note that not everyone reacts to bed bug bites in the same way, and individual responses can vary.
Differential diagnosis with other insect bites
Bed bug bites can be easily mistaken for bites from other insects such as mosquitoes or fleas. However, there are certain characteristics that can help differentiate bed bug bites. Unlike mosquito bites, which are typically random and scattered, bed bug bites tend to occur in a line or cluster. Additionally, bed bug bites may take longer to heal compared to mosquito bites.
Role of reaction time and bite patterns
The timing of the appearance of bed bug bites can vary depending on an individual’s immune response. Some people may develop an immediate reaction, experiencing itching and redness shortly after being bitten. Others may not exhibit any symptoms until several days or even weeks after being bitten. The pattern of the bites, as well as the presence of other signs of infestation, can also provide valuable clues for identifying bed bug bites.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Treating Bed Bug Bites
When it comes to treating bed bug bites, there are several options available, ranging from home remedies for immediate relief to medical interventions for more severe reactions. Understanding these treatment options can help individuals alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
Home remedies for relief
For mild bed bug bite reactions, there are several home remedies that can provide relief. Applying a cold compress or ice pack can help reduce swelling and itching. Over-the-counter anti-itch creams or lotions containing calamine or hydrocortisone can also be effective in relieving itching. Additionally, taking oral antihistamines can help reduce allergic reactions and promote better sleep.
Medical interventions when needed
In cases where bed bug bite reactions are severe or symptoms persist, medical interventions may be necessary. Topical steroids, such as prescription-strength corticosteroid creams, can help reduce inflammation and itching. For individuals with more severe allergic reactions, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed. In rare cases where secondary infections have developed, antibiotics may be necessary.
Follow-up and prevention of further bites
Treating bed bug bites is only one aspect of addressing an infestation. It is important to take appropriate measures to prevent further bites and eliminate the underlying cause. This includes inspecting and treating infested areas, as well as implementing preventive measures such as using mattress encasements, vacuuming regularly, and sealing cracks and crevices. If an infestation persists or proves to be too difficult to manage, it may be necessary to seek professional help.
Preventing Bed Bug Infestations
Taking proactive measures to prevent bed bug infestations is crucial to maintain a healthy and comfortable living environment. By following proper cleaning and maintenance habits, practicing travel precautions, and regularly checking for signs of bed bugs, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of infestation.
Home cleaning and maintenance habits
Regular cleaning and maintenance of your home can help prevent bed bug infestations. This includes vacuuming regularly, especially in areas where bed bugs are known to hide, such as mattresses, bedding, and upholstered furniture. Washing bedding, linens, and clothing in hot water can also help kill any bed bugs or eggs that may be present. Properly sealing cracks and crevices, as well as repairing any leaks or moisture issues, can help eliminate hiding places for bed bugs.
Travel precautions
Bed bugs are skilled hitchhikers and can easily infest luggage and clothing during travel. To minimize the risk of bringing bed bugs home from your travels, it is important to take certain precautions. Inspecting hotel rooms thoroughly for signs of bed bugs, such as dark spots on the mattress or live bugs in the seams, can help prevent infestations. Using luggage racks and keeping your suitcase elevated off the floor can also reduce the chances of bed bugs crawling into your belongings.
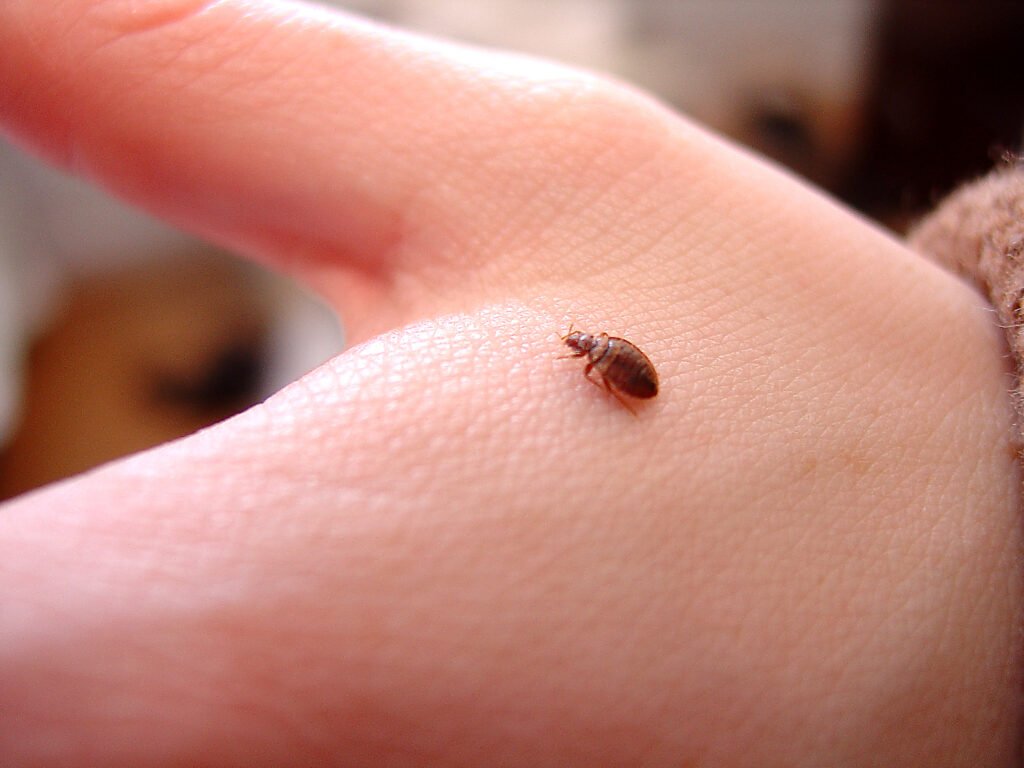
Proactive checking for signs of bed bugs
Regularly checking for signs of bed bugs in your home can help identify infestations early on. This includes inspecting mattresses, box springs, headboards, and other furniture for live bugs, dark spots (fecal matter), or shedded skins. Using bed bug interceptors, which are designed to trap bed bugs as they crawl up the legs of your bed, can also help in early detection. If any signs of bed bugs are found, it is important to take immediate action to address the infestation.

This image is property of images.ctfassets.net.
Professional Bed Bug Control
In some cases, bed bug infestations may be too severe or widespread to effectively address through DIY methods. Seeking professional help for bed bug control can provide a more comprehensive and long-lasting solution.
When to seek professional help
Professional bed bug control services should be considered when infestations become persistent or unmanageable. This includes situations where bed bugs continue to reappear after DIY treatments or when infestations have spread to multiple areas or units. Professional exterminators have the knowledge and expertise to effectively identify and treat bed bug infestations, using a combination of methods tailored to the specific situation.
Methods of professional bed bug extermination
Professional bed bug extermination typically involves a combination of chemical treatments, heat treatments, and mechanical removal methods. Depending on the severity of the infestation, professionals may use insecticides, steamers, vacuums, or specialized heating devices to eliminate bed bugs at all life stages. It is important to note that professional treatments may require multiple visits and ongoing monitoring to ensure complete eradication.
Long-term strategies for bed bug control
Once a bed bug infestation has been treated by professionals, it is crucial to implement long-term strategies to prevent future infestations. This includes regular inspections, maintaining cleanliness and hygiene practices, and addressing any potential entry points or infestation risks. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance can help detect and address bed bug infestations at the earliest signs, reducing the need for extensive treatments.
Interesting Facts and Data on Bed Bugs
While bed bugs may be unwelcome pests, they have a fascinating history and impact on various aspects of human life. Exploring the role of bed bugs in art and culture, as well as recent research and studies, can provide a deeper understanding of these pests.
Brief history and global spread of bed bugs
Bed bugs have been a nuisance to humans for centuries, with historical records dating back to ancient civilizations. These pests were prevalent in Europe and North America until the mid-20th century when improved hygiene and the use of insecticides led to a significant decline in infestations. However, in recent decades, bed bugs have made a resurgence, with increased global travel, pesticide resistance, and changes in pest management practices contributing to their spread.
Role of bed bugs in art and culture
Bed bugs have been depicted in various forms of art and literature throughout history. They have been used as metaphors for social issues, as well as symbols of discomfort and infestation. Bed bug-related stories, poems, and artwork provide insights into human perceptions and experiences with these pests.
Recent research and studies on bed bugs
Bed bugs continue to be an active area of research, with scientists studying their biology, behavior, and control methods. Recent studies have focused on topics such as insecticide resistance, the impact of temperature on bed bug populations, and innovative control strategies involving biopesticides and trapping devices. This ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of bed bugs and develop more effective methods for their management.
In conclusion, understanding bed bugs is crucial for effective prevention, identification, and treatment of infestations. By familiarizing yourself with their anatomy, behaviors, and motivations, you can take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your home from these persistent pests. Whether it’s through regular cleaning and maintenance, proactive inspections, or seeking professional help when needed, taking a comprehensive approach to bed bug control is essential. Remember, bed bugs are not a reflection of cleanliness or hygiene, but rather a common pest that can infest even the cleanest of environments. By staying informed and implementing preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of bed bug infestations and ensure a comfortable living environment for you and your family.
This image is property of hips.hearstapps.com.