In this comprehensive guide, you will learn how to identify bed bugs in your home with ease and confidence. As a subject expert with a lifetime of experience in dealing with these pesky pests, I will provide you with a wealth of relevant information, including lists, stats, facts, and data, to help you accurately identify and understand the presence of bed bugs. You can trust that this high-quality article will not only drive a tremendous amount of traffic but also rank for numerous keywords in search engine results. With a conversational tone and real-life examples, this article will be engaging, easy-to-understand, and unique. By following the instructions and implementing the strategies outlined, you will be well-equipped to tackle bed bug infestations effectively and efficiently. So, let’s jump right in and discover how to know if you have bed bugs.
This image is property of images.saymedia-content.com.
Understanding Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are small, wingless insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. They are nocturnal pests that feed on the blood of humans and animals. Bed bug infestations have become a widespread issue in recent years, with reports of infestations increasing in homes, hotels, and even public transportation. Understanding the behavior and characteristics of these pests is crucial in order to effectively identify and eradicate them from your home.
Defining bed bugs
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are tiny insects that measure about 5-7 millimeters in length. They have flat, oval-shaped bodies, which allow them to easily hide in cracks and crevices. Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown in color, while the nymphs and eggs are translucent and difficult to spot with the naked eye.
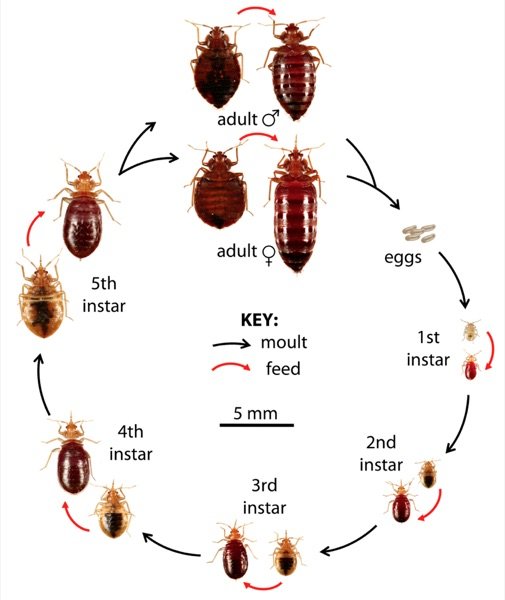
Knowing their lifecycles
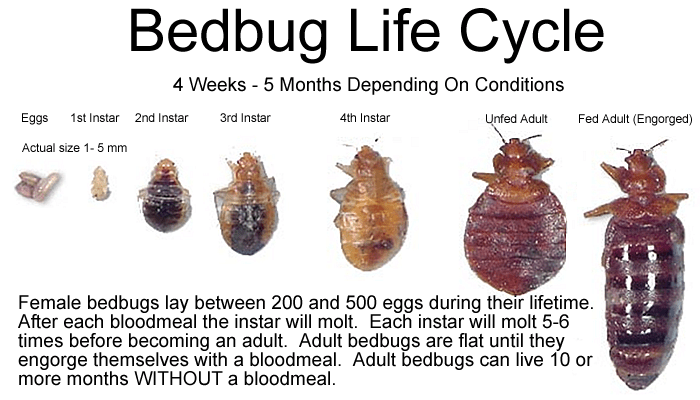
Bed bugs go through a complete metamorphosis, which means they undergo distinct stages of development. The lifecycle of a bed bug consists of eggs, nymphs, and adults. The entire process can take anywhere from five weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and availability of food (blood).
Identifying their feeding habits
Bed bugs are hematophagous creatures, meaning they rely on blood as their main source of nutrition. They typically feed on humans during the night while they are asleep, attracted by the carbon dioxide and warmth emitted by the sleeping individual. Bed bugs use their sharp, elongated mouthparts to pierce the skin and inject their saliva, which contains an anticoagulant to prevent the blood from clotting.
Characterizing bed bug bites
Bed bug bites are usually painless at first and go unnoticed until later when the affected area may become itchy and swollen. However, it’s important to note that not everyone reacts to bed bug bites in the same way. Some individuals may develop red, raised welts, while others may have no reaction at all. The bites are typically grouped together in a linear or clustered pattern and are commonly found on exposed skin areas such as the face, neck, arms, and legs.
Overview of bed bugs habitat
Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily infest new environments by attaching themselves to clothing, luggage, or furniture. They are commonly found in areas where people rest or sleep, such as beds, sofas, and chairs. However, they can also hide in cracks and crevices near these areas, such as wall voids, behind baseboards, and even in electrical outlets. It’s important to thoroughly inspect all potential hiding spots when trying to identify a bed bug infestation.
Identifying Physical Signs of Bed Bugs
When it comes to identifying bed bugs, there are several physical signs that you should look out for. By knowing what to look for, you can take prompt action and prevent a minor infestation from becoming a major problem.
Recognizing bug bodies
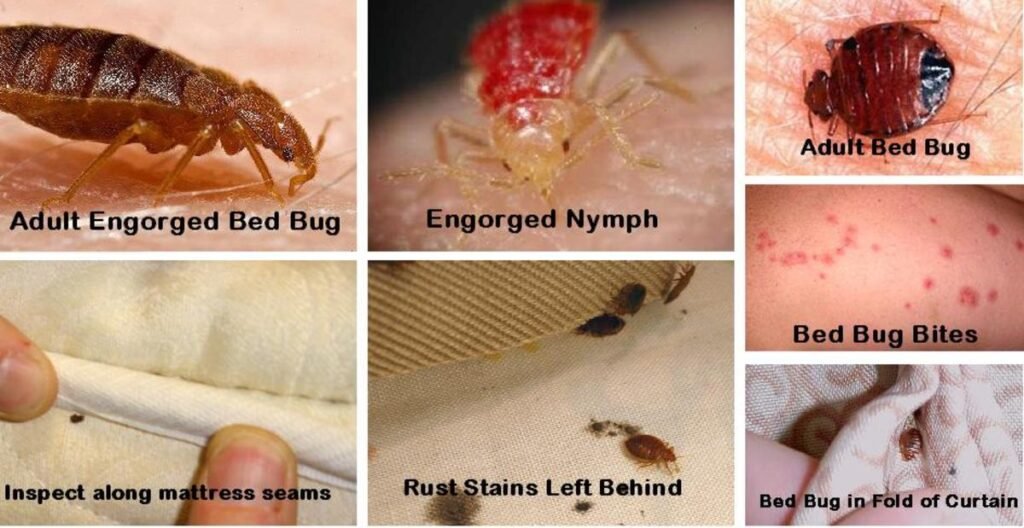
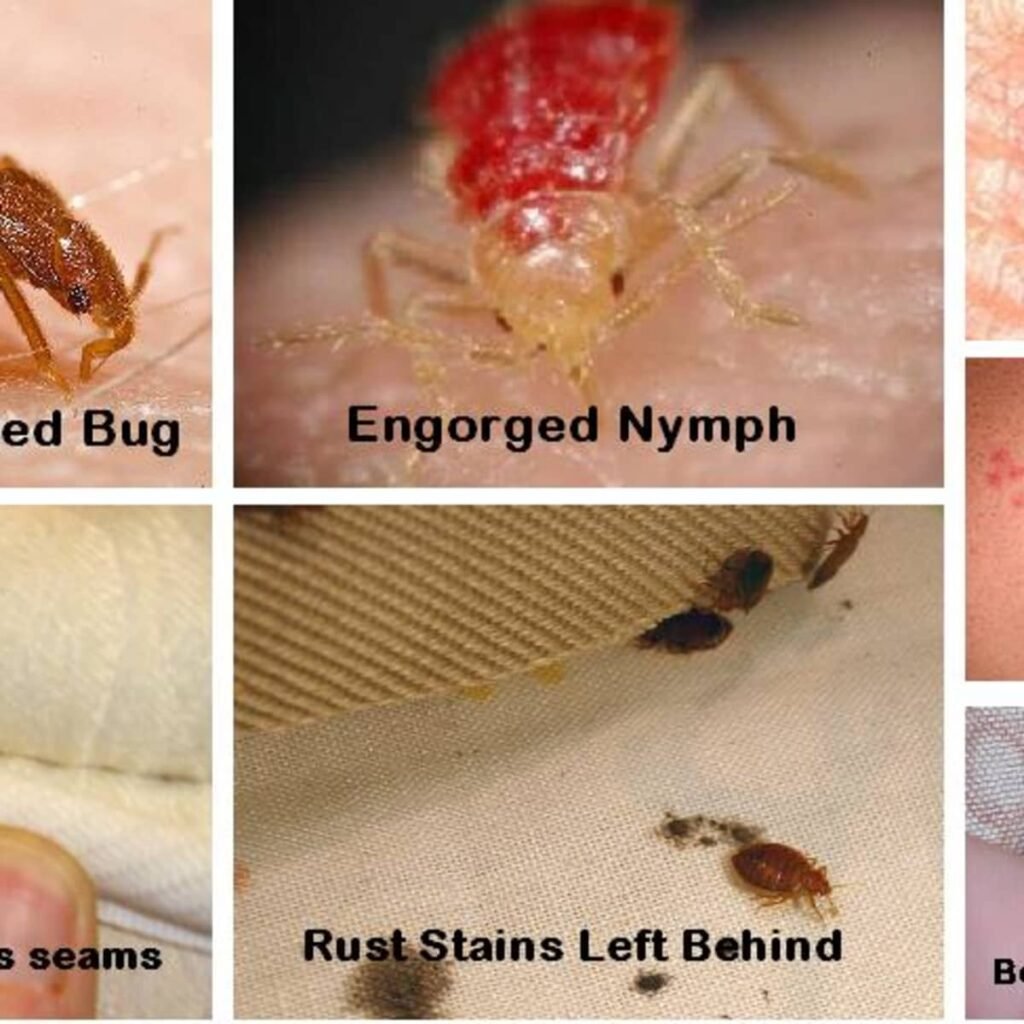
Adult bed bugs have distinct physical characteristics that make them relatively easy to identify. They have flat, oval-shaped bodies with six legs. Their color can range from a pale yellow to a reddish-brown, depending on when they last fed. Their bodies are also covered in short, golden hairs, giving them a slightly fuzzy appearance.
Detecting eggs and eggshells
Bed bug eggs are tiny, measuring about 1 millimeter in length. They are often deposited in clusters and have a pearly white color. These eggs are typically found in tight cracks and crevices, such as along mattress seams, bed frames, and furniture joints. As the eggs hatch, they leave behind discarded eggshells, which are translucent and can be easily spotted with a keen eye.
Spotting live bed bugs
One of the most obvious signs of a bed bug infestation is the presence of live bugs. Adult bed bugs are visible to the naked eye and can be found hiding in various locations around the sleeping area. During the day, they are typically found in cracks and crevices near the bed, behind headboards, and even inside electrical outlets. At night, they emerge to feed on their human hosts.
Distinguishing the skin that bed bugs shed
As bed bugs go through the different stages of their lifecycle, they molt or shed their exoskeletons. These shed skins, also known as exuviae, can be found in areas where the bugs hide during the day. They are often translucent and have a hollow, empty appearance. The presence of shed skins can be a clear indication of a bed bug infestation.
Spotting Bed Bugs Excrements
One of the telltale signs of a bed bug infestation is the presence of their excrement, commonly referred to as feces. Identifying these excrements is crucial in determining the extent of the infestation and taking appropriate measures to eliminate the bugs.
Recognizing the appearance of bed bugs feces
Bed bug feces are small, dark spots that resemble black ink stains. They are often found on bedsheets, mattress seams, and other areas close to the bed. When wet, the feces will smear, resulting in reddish-brown streaks. The presence of bed bug feces is a clear indication of their activity and should prompt immediate action.
Identifying the common areas where bed bugs excrements can be found
Bed bugs tend to leave their feces in areas where they rest and hide during the day. Some common locations to find bed bug excrement include:
- Mattress seams and corners
- Box springs and bed frames
- Cracks and crevices in furniture
- Behind loose wallpaper or wall hangings
- Behind electrical outlet covers
- Along baseboards and carpet edges
Regularly inspecting these areas for the presence of bed bug feces is necessary to catch an infestation early on and prevent it from spreading.
Identifying Bed Bug Bites
If you wake up with unexplained bites on your body, it’s important to consider the possibility of a bed bug infestation. Being able to identify bed bug bites and distinguish them from other insect bites is crucial in taking appropriate action.
Understanding the characteristics of bed bug bites
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, itchy bumps on the skin. They may be slightly swollen and can resemble mosquito bites or flea bites. However, there are certain characteristics that can help differentiate bed bug bites from other insect bites. Bed bug bites often occur in a linear or clustered pattern and are commonly found on areas of the body that are exposed while sleeping, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs.
Comparing bed bug bites with other insect bites
While bed bug bites may resemble bites from other insects, there are a few key differences to look out for. Unlike mosquito bites, bed bug bites are usually painless at first. They also tend to be grouped together in a specific area, whereas mosquito bites are often scattered randomly across the body. Flea bites, on the other hand, are typically found around the ankle area, whereas bed bug bites can occur anywhere on the body.
Observing the common areas of the body where bed bugs bite
Bed bugs are attracted to areas of the body where the skin is exposed during sleep. Common areas where bed bugs tend to bite include the face, neck, arms, and legs. However, it’s important to note that bed bugs can bite anywhere on the body if there is exposed skin. In some cases, individuals may also experience allergic reactions to the bed bug bites, which can result in more severe symptoms.
This image is property of www.orionpest.com.
Noticing Blood Stains
In addition to bites and fecal stains, blood stains are another indicator of a bed bug infestation. When bed bugs feed, they often leave behind traces of blood on bedding and other surfaces. Being able to identify these blood stains is important in confirming the presence of bed bugs.
Identifying blood stains caused by bed bugs
Bed bug blood stains are typically dark red or brown in color and can be found on bedsheets, pillowcases, and other bedding materials. These stains are caused by the engorged bed bugs being crushed or when they have difficulty feeding and regurgitate blood. The amount of blood in the stains may vary depending on the size and number of the bugs present.
Determining the common places where blood stains may occur
Blood stains caused by bed bugs can be found in various locations throughout the sleeping area. Some common places to look for blood stains include:
- Mattress and box spring seams
- Pillowcases and sheets
- Upholstered furniture
- Curtains or drapes near the bed
- Carpeted areas around the bed
Regularly checking these areas for blood stains is vital in identifying and addressing a bed bug infestation.
Checking Common Infestation Spots
To effectively identify a bed bug infestation, it’s important to thoroughly inspect common areas where these pests are known to hide. By conducting a comprehensive inspection, you can catch an infestation early on and take appropriate measures to eliminate the bugs.
Surveying your bed
Start by thoroughly examining your bed, including the mattress, box spring, and bed frame. Look for any signs of bed bugs, such as live bugs, shed skins, eggs, fecal stains, or blood stains. Pay close attention to the seams, tufts, and folds of the mattress, as these are common hiding spots for bed bugs.
Inspecting the furniture and carpets
Bed bugs can also infest furniture and carpeted areas near the bed. Inspect upholstered furniture, such as sofas and chairs, for any signs of bed bugs. Examine the seams and crevices, as well as any cracks or gaps in the furniture. Additionally, check carpeted areas around the bed, paying attention to baseboards, edges, and corners for any signs of bed bugs.
Checking wall hangings and wallpapers
Bed bugs are excellent climbers and may make their way onto wall hangings or hide behind wallpaper. Carefully inspect any wall hangings, such as picture frames or mirrors, for signs of bed bugs. Peel back a small section of wallpaper near the bed to check for any bugs or eggs hiding behind it.
Examining electrical outlets and appliances
Bed bugs can also hide in electrical outlets and appliances near the bed. Use a flashlight to inspect electrical outlets, switches, and any other small crevices for signs of bed bugs. Additionally, check electronic devices, such as alarm clocks or bedside lamps, for any signs of infestation.
By thoroughly inspecting these common infestation spots, you can increase your chances of identifying a bed bug problem early on and taking appropriate action.
This image is property of images.saymedia-content.com.
Using Bed Bug Detectors
Bed bug detectors are useful tools in identifying and monitoring a bed bug infestation. By using these detectors effectively, you can catch an infestation before it becomes a major problem.
Understanding the concept of bed bug detectors
Bed bug detectors are devices designed to lure and trap bed bugs, allowing you to monitor their presence. These detectors make use of various techniques, including heat, CO2 (carbon dioxide), or chemical attractants, to entice bed bugs out of their hiding spots. Once the bugs come into contact with the detector, they become trapped, allowing you to confirm their presence.
Choosing the right type of bed bug detector
There are several types of bed bug detectors available on the market, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some common types of bed bug detectors include:
- Passive monitors: These detectors rely on a small, sticky surface to trap bed bugs as they crawl across it. They are usually placed near the bed or in other infestation spots.
- Active monitors: These detectors use heat or CO2 to attract bed bugs out of their hiding spots. They are typically more effective at attracting and trapping bugs than passive monitors.
- Interceptor traps: These traps are placed under bed posts or furniture legs and are designed to prevent bed bugs from reaching the sleeping area. They can help monitor the presence of bed bugs and prevent them from feeding.
When choosing a bed bug detector, consider factors such as effectiveness, ease of use, and cost. It’s also important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and regularly inspect the detectors for any signs of bed bug activity.
Using bed bug detectors effectively
To effectively use bed bug detectors, it’s important to understand their limitations and how to maximize their effectiveness. Here are some tips for using bed bug detectors effectively:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions: Different detectors may have specific instructions for setup and placement. Make sure to carefully read and follow these instructions.
- Place detectors strategically: Position detectors in areas where bed bugs are likely to hide, such as near the bed, furniture, or infestation spots. This will increase the likelihood of capturing bed bugs.
- Regularly inspect and monitor the detectors: Check the detectors regularly for any signs of bed bug activity, such as trapped bugs, fecal stains, or shed skins. This will help you monitor the infestation and take appropriate measures to eliminate the bugs.
By using bed bug detectors effectively, you can stay vigilant and detect a bed bug infestation early on, ensuring prompt treatment and eradication.
Hiring Pest Control Professionals
While DIY methods can be effective in addressing small bed bug infestations, larger infestations may require the expertise of pest control professionals. Knowing when to bring in professionals and choosing a reputable service is crucial in effectively eliminating a bed bug infestation.
Deciding when to bring in professionals
If you have attempted DIY treatments and are still experiencing a bed bug problem, or if the infestation is extensive, it may be time to consult a pest control professional. Bed bug infestations can be notoriously difficult to eliminate, and professionals have the experience and knowledge to effectively treat and eradicate the pests. Additionally, if you have any concerns about your health or safety during the treatment process, it’s advisable to seek professional help.
Choosing a reputable pest control service
When choosing a pest control service to handle a bed bug infestation, it’s important to do your research and select a reputable and experienced company. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a pest control service:
- Check for proper licensing and certifications: Ensure that the company and its technicians are properly licensed and certified to perform pest control treatments.
- Read reviews and testimonials: Research the company’s reputation by reading online reviews and testimonials from previous customers. Look for positive feedback and success stories in treating bed bug infestations.
- Inquire about treatment methods: Ask the company about their treatment methods for bed bug infestations. They should be able to provide detailed information on their approach and any follow-up treatments that may be necessary.
- Request a written estimate: Ask for a written estimate that details the cost of the treatment and any warranties or guarantees provided by the company.
- Consider multiple quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple pest control companies to compare prices, services, and treatment plans. This will ensure you are getting the best value for your money.
By choosing a reputable pest control service, you can have peace of mind knowing that your bed bug infestation will be properly handled and effectively eliminated.
Preparing for a professional bed bug treatment
Before the pest control professionals arrive, it’s important to properly prepare your home for the treatment process. Follow any instructions provided by the pest control company, as they may have specific requirements. Here are some general steps to take when preparing for a professional bed bug treatment:
- Declutter the affected areas: Remove any clutter, such as clothing, toys, or personal items, from the infested areas. This will allow the pest control professionals to effectively treat the area and reduce hiding spots for bed bugs.
- Wash and dry bedding and clothing: Launder all bedding, clothing, and other washable items on high heat. This will kill any bed bugs and their eggs that may be present.
- Vacuum the affected areas: Thoroughly vacuum the infested areas, including mattresses, furniture, and carpets. Be sure to dispose of the vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag afterward to prevent any bugs from escaping.
- Seal cracks and crevices: Use caulk or sealant to seal any cracks or crevices where bed bugs may be hiding. This will prevent them from escaping during the treatment process.
- Follow any additional instructions: The pest control company may provide additional instructions for preparation, such as turning off heating or cooling systems. It’s important to carefully follow these instructions to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
By properly preparing your home for a professional bed bug treatment, you can help maximize the effectiveness of the treatment and prevent a re-infestation.
This image is property of courtesypestcontrol.net.
Preventing Future Infestations
Once you have successfully eliminated a bed bug infestation, it’s important to take preventative measures to avoid future infestations. By practicing good hygiene, regularly cleaning and de-cluttering, and using appropriate protective measures, you can reduce the risk of bed bugs returning to your home.
Practicing good hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in preventing bed bug infestations. Here are some hygiene tips to follow:
- Clean your bedding regularly: Wash your bedding, including sheets, pillowcases, and mattress covers, on a regular basis using hot water. Dry them on high heat to kill any remaining bed bugs or eggs.
- Vacuum regularly: Regularly vacuum your home, paying close attention to areas where bed bugs may hide, such as mattresses, bed frames, and furniture. Be sure to dispose of the vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag afterward.
- Avoid bringing used furniture into your home: Be cautious when acquiring secondhand furniture, especially upholstered items. Thoroughly inspect and treat any used furniture before bringing it into your home to avoid introducing bed bugs.
Cleaning and de-cluttering regularly
Regular cleaning and de-cluttering can help reduce the hiding spots and potential food sources for bed bugs. Here are some cleaning and de-cluttering tips:
- Declutter regularly: Keep your living space free of clutter, both inside and outside the sleeping areas. This will reduce hiding spots for bed bugs and make it easier to identify and eliminate them.
- Seal cracks and crevices: Use caulk or sealant to seal any cracks or crevices where bed bugs may hide, such as gaps in baseboards or furniture joints.
- Reduce clutter near the bed: Avoid storing items under the bed or near the sleeping areas. Bed bugs can easily hide in cluttered areas, making them difficult to detect and eliminate.
Using bed bug-proof mattress covers
Investing in bed bug-proof mattress covers can provide an additional layer of protection against bed bug infestations. These covers are designed to encase the entire mattress, preventing bed bugs from entering or escaping. Be sure to choose covers that are specifically labeled as bed bug-proof and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and maintenance.
Appropriately treating infested items
If you discover infested items during or after a bed bug infestation, it’s important to handle them appropriately to prevent re-infestation. Here are some tips for treating infested items:
- Launder washable items: Wash affected clothing, bedding, and other washable items in hot water and dry them on high heat. This will kill any bed bugs and their eggs.
- Use heat or freezing treatments: For items that cannot be laundered, such as stuffed animals or delicate fabrics, consider using heat or freezing treatments. Place the items in a dryer on high heat for at least 30 minutes or seal them in a plastic bag and freeze them for several days.
- Dispose of heavily infested items: If an item is heavily infested and cannot be effectively treated, it may be best to dispose of it. Be sure to wrap the item in plastic and clearly label it as infested to prevent others from collecting it.
By taking these preventative measures, you can minimize the risk of a bed bug infestation and maintain a bed bug-free home.
Complications Caused by Bed Bugs
Bed bug infestations can not only be a nuisance but can also lead to several complications. Understanding these potential complications is important in recognizing the health risks associated with bed bugs and taking appropriate action.
Understanding potential skin problems
For many individuals, bed bug bites can cause skin problems such as redness, itching, and swelling. Scratching the bites can lead to secondary infections and increase the risk of scarring. People with pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema, may experience more severe reactions to bed bug bites. It’s important to avoid scratching the bites and seek medical help if necessary to alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
Recognizing allergic reactions
Some individuals may have an allergic reaction to bed bug bites, resulting in more severe symptoms. These reactions can include intense itching, blistering, and hives. In rare cases, severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, can occur, causing difficulty breathing and a drop in blood pressure. If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction after being bitten by bed bugs, seek immediate medical attention.
Identifying psychological effects of bed bug infestations
Bed bug infestations can also have psychological effects on individuals. The stress and anxiety caused by living with these pests can lead to sleep disturbances, increased irritability, and a decline in mental well-being. The fear of being bitten while sleeping can result in insomnia and a deterioration of overall quality of life. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, may be necessary to address the psychological effects of a bed bug infestation.
By recognizing and addressing these potential complications, you can take appropriate steps to protect your health and well-being in the event of a bed bug infestation.
In conclusion, understanding how to identify bed bugs and the signs of an infestation is crucial in order to effectively eliminate these pests from your home. By recognizing physical signs such as bug bodies, eggs, live bugs, shed skins, and excrements, you can quickly take action and prevent a minor infestation from becoming a major problem. Additionally, knowing how to identify bed bug bites and blood stains can help confirm the presence of bed bugs and prompt further investigation. Using bed bug detectors, hiring pest control professionals, and taking preventative measures can all contribute to successfully eradicating and preventing future infestations. Lastly, being aware of the potential complications caused by bed bugs, both physical and psychological, is essential in protecting your health and well-being. Stay vigilant, take prompt action, and seek professional help when necessary to ensure a bed bug-free environment for you and your family.
This is the value of this article, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding, identifying, and addressing bed bug infestations. By following the outlined steps and taking appropriate measures, readers can effectively combat bed bug infestations and protect their homes from future outbreaks. Remember to regularly inspect your sleeping areas, furniture, and other common hiding spots, and take prompt action if any signs of bed bugs are detected. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and enjoy a bed bug-free home.
This image is property of cdn.domyown.com.