Why are bed bugs so difficult to get rid of? Bed bugs, tiny insects that feed on human blood, have been a nuisance for centuries. Despite advancements in pest control methods, these resilient pests continue to thrive. The challenge lies in their ability to hide and multiply rapidly, making them difficult to detect and eliminate. Bed bugs are skilled at hiding in cracks and crevices, such as mattress seams, furniture, and walls, only emerging at night to feed on unsuspecting human hosts. Their small size, ability to withstand extreme temperatures, and resistance to many conventional pesticides further contribute to their tenacity. Eradicating bed bugs requires a comprehensive and meticulous approach, involving thorough inspection, targeted treatment, and ongoing monitoring. In this article, we will delve into the reasons why bed bugs are so difficult to eradicate and provide valuable insights to help you combat these persistent pests.

Understanding Bed Bugs
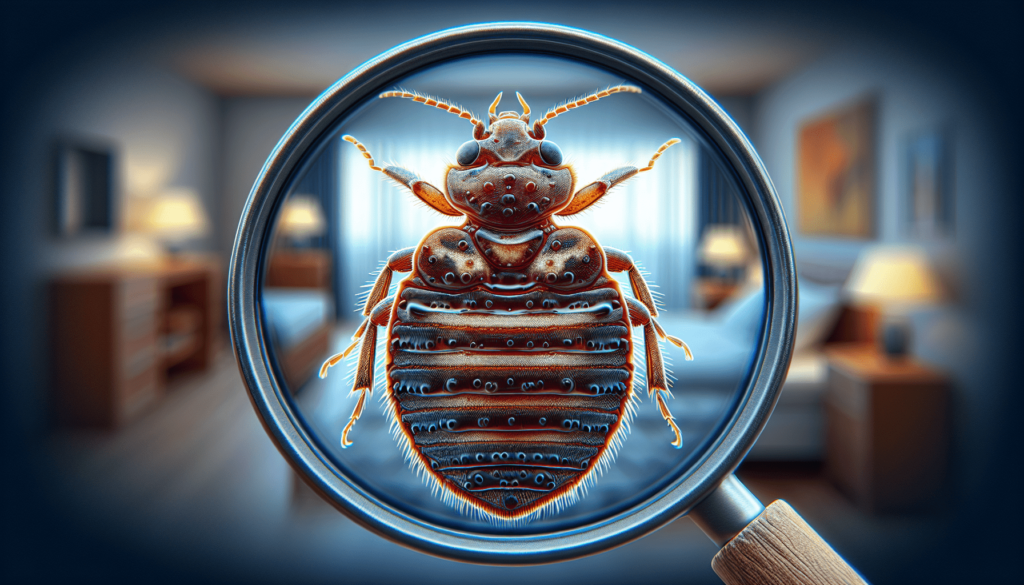
Bed bugs are small, parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are reddish-brown in color and have flat, oval-shaped bodies, reaching about the size of an apple seed when fully grown. Despite their small size, bed bugs can cause significant frustration and stress when they infest homes and other living spaces.
Bed bug basic characteristics
Bed bugs are ectoparasites, meaning they live on the outside of their host’s body. They are primarily active at night and tend to hide during the day. They are attracted to warm-blooded animals for feeding, with humans being their preferred host. Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily latch onto clothing, luggage, or other items, allowing them to spread rapidly from one location to another.
Natural habitats and preferred conditions
While bed bugs are often associated with infestations in beds and mattresses, they can be found in a variety of locations. They can hide in furniture, cracks and crevices, electrical outlets, and even behind wallpaper. Bed bugs are skilled at finding hiding spots that provide them with both easy access to their host and protection from detection and extermination efforts.
As for preferred conditions, bed bugs thrive in environments with temperatures between 70 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit. They can survive in lower temperatures, but it will take them longer to develop and reproduce. Additionally, bed bugs require a source of food, which is the blood of humans or animals, to survive and reproduce.
Bed bug life cycle and reproduction
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is crucial for effective pest control. Adult female bed bugs can lay up to five eggs per day, totaling around 200 to 500 eggs over their lifetime. These eggs are small, about the size of a pinhead, and are typically laid in cracks and crevices near the host’s sleeping area.
After hatching, bed bug nymphs go through five developmental stages, known as instars, before reaching adulthood. Each stage requires a blood meal, and the time it takes for a bed bug to progress from one stage to the next depends on various factors, including temperature and food availability. On average, it takes bed bugs about five to eight weeks to develop from egg to adult.
Once bed bugs reach adulthood, they will continue to reproduce, perpetuating the infestation if not effectively controlled.
Why Bed Bugs Are Attracted to Your Home
Understanding why bed bugs are attracted to your home is essential in preventing infestations and implementing effective control measures.
Bed bugs attraction to human presence
Bed bugs are attracted to the carbon dioxide and warmth emitted by humans and animals. When we sleep, our bodies produce these signals, which act as beacons for bed bugs looking for a blood meal. Additionally, bed bugs are drawn to the pheromones we emit, making our homes an ideal environment for them to thrive.
Ideal conditions in homes for bed bugs
Homes provide the ideal conditions for bed bugs to establish themselves. Our homes offer shelter, warmth, and a readily available food source. Bed bugs can easily hide in furniture, bedding, and other household items, making it challenging to detect and eliminate them. Furthermore, the ability of bed bugs to survive for several months without feeding allows them to patiently wait for the opportune moment to feed on a sleeping host.
Common hiding spots for bed bugs in homes
Bed bugs are skilled at finding hiding spots in homes, allowing them to remain undetected for extended periods. Some common hiding spots for bed bugs include:
- Mattresses and box springs: Bed bugs often hide in the seams and crevices of mattresses and box springs, as they provide easy access to a sleeping host.
- Bed frames and headboards: Bed bugs can hide in cracks and crevices in bed frames and headboards, making these areas hotspots for infestations.
- Furniture: Upholstered furniture, such as couches and chairs, can provide an ideal hiding spot for bed bugs. They can hide in the cushions, seams, and even behind the furniture.
- Electrical outlets and baseboards: Bed bugs can squeeze into tight spaces, including electrical outlets and gaps behind baseboards, making them challenging to detect.
- Luggage and personal belongings: Bed bugs can hitch a ride on luggage, clothing, and other personal belongings, allowing them to infest new locations when these items are brought into a home.
Bed Bug Bites and Health Implications
Bed bug bites can cause a range of health implications, both physically and psychologically. Understanding the signs of bed bug bites and their potential risks is crucial for prompt identification and treatment.
Identifying bed bug bites
Bed bug bites often appear as small, red welts or raised bumps on the skin. They are typically grouped together in a line or cluster, often resembling a rash. However, it is important to note that not everyone reacts to bed bug bites in the same way. Some individuals may have minimal or no reaction at all, while others may experience intense itching and allergic reactions.
Health risks associated with bed bug bites
While bed bug bites themselves are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can lead to secondary complications. Excessive scratching of the bites can cause skin infections, which may require medical intervention. Additionally, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to bed bug bites, resulting in severe itching, swelling, and even difficulty breathing in rare cases.
Physiological effects of bed bug infestations
In addition to the physical effects of bed bug bites, infestations can also have psychological implications. The presence of bed bugs in a home can lead to stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. The constant fear of being bitten and the associated stigma can have a significant impact on the mental well-being of individuals and families affected by bed bug infestations.
The Difficulty of Detecting Bed Bugs
Detecting bed bugs can be incredibly challenging due to their elusive nature and small size. Understanding the difficulties associated with detection is crucial for effective pest control.
Tiny size and nocturnal behavior of bed bugs
Bed bugs are tiny, ranging from 1 to 7 millimeters in length. Their small size allows them to hide in narrow cracks and crevices, making them difficult to spot with the naked eye. Furthermore, bed bugs are primarily active at night when their hosts are asleep, further complicating the detection process.
Ability to stay hidden and undetected
Bed bugs have evolved to be excellent at hiding in various environments. They can squeeze into tiny spaces, such as electrical outlets, and remain hidden during the day. Their flat bodies allow them to fit into cracks and crevices, making it challenging to locate and eliminate them.
Misdiagnosis of bed bug bites
One of the challenges in detecting bed bugs is misdiagnosing their bites. Bed bug bites can resemble bites from other pests, such as mosquitoes or fleas. This misdiagnosis can lead to delayed or ineffective treatment, allowing the infestation to worsen.

Bed Bugs’ Resistance to Insecticides
Bed bugs have developed resistance to many common insecticides over the years, further complicating their eradication. Understanding the history and contributing factors to this resistance is essential for effective pest control.
History of bed bug resistance to common insecticides
Bed bugs have shown resistance to various classes of insecticides, including pyrethroids, which are commonly used in bed bug treatments. This resistance has been documented since the late 1990s and has continued to increase over time. The widespread use of insecticides and their subpar efficacy in eradicating bed bug infestations have contributed to the development of resistance.
Genetic factors contributing to insecticide resistance
Genetic mutations play a significant role in bed bug resistance to insecticides. These mutations can alter the target sites of the insecticides or enhance the ability of the bed bugs to detoxify or eliminate the insecticides from their bodies. Additionally, the rapid reproduction of bed bugs allows resistant individuals to pass on their genetic traits to future generations, further perpetuating resistance.
New threats: Super bed bugs
The emergence of “super bed bugs” has raised concerns in recent years. These bed bugs have developed resistance to multiple classes of insecticides, making them even more challenging to control. The increase in global travel and the ease of spreading bed bugs have contributed to the rapid spread of these resistant populations.
Bed Bugs’ Rapid Reproduction
The reproductive capabilities of bed bugs contribute to the rapid spread and persistence of infestations. Understanding their reproductive cycle and survival rates is crucial for effective control.
Short reproductive cycle
Bed bugs have a relatively short reproductive cycle, allowing for rapid population growth. Female bed bugs can start laying eggs as early as five to ten days after their first blood meal. This short time frame means that a small infestation can quickly escalate into a significant problem if left untreated.
High egg output of female bed bugs
Female bed bugs are prolific egg layers, capable of producing up to five eggs per day. Over their lifetime, a female bed bug can lay hundreds of eggs. This high egg output further contributes to the exponential growth of infestations, making it essential to detect and address bed bug populations as early as possible.
Survival rates of baby bed bugs
Baby bed bugs, also known as nymphs, have a high survival rate under favorable conditions. They can survive for several months without feeding, allowing them to wait for the opportune moment to obtain a blood meal. Their ability to lay dormant for extended periods makes it challenging to eliminate all bed bugs in an infested area without thorough and targeted treatments.
Bed Bugs’ Ability to Go Without Feeding
Bed bugs have developed survival mechanisms that allow them to go without feeding for extended periods. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial when developing effective control strategies.
Survival mechanisms in bed bugs during starvation periods
During periods of starvation, bed bugs can enter a state of torpor, reducing their metabolic rate and conserving energy. This torpor allows them to survive for several months without feeding, waiting for a host to become available. Bed bugs can also exhibit a phenomenon called “cryptobiosis,” where they enter a dormant state and can withstand extreme temperatures and other adverse conditions.
Consequences of intermittent feeding on control methods
The ability of bed bugs to go without feeding for extended periods poses challenges for control methods that rely on the presence of a host. Traditional insecticides and treatments may not be effective against bed bugs in a dormant state, as they do not come into contact with the treatments. This intermittent feeding behavior can prolong infestations and require multiple treatment approaches to achieve complete eradication.
Effect on life cycle and reproduction
Intermittent feeding can also impact the life cycle and reproduction of bed bugs. When a blood meal is scarce, bed bugs can delay their reproductive cycle, reducing the number of eggs laid. This adaptive behavior ensures that their reproductive efforts align with the availability of a suitable host, allowing them to increase their chances of successful reproduction.
Ineffective DIY Bed Bug Control Methods
Many individuals attempt to eliminate bed bug infestations using do-it-yourself (DIY) methods. However, these methods often fall short in fully eradicating the infestation. Understanding the limitations of common DIY methods is essential to make informed decisions about pest control.
Commonly recommended DIY methods and their shortcomings
Heat treatments, vacuuming, and steam treatments are commonly recommended DIY methods for bed bug control. While these methods can help reduce the bed bug population, they often fail to fully eliminate the infestation. Bed bugs can easily hide in inaccessible areas, leading to incomplete eradication. Additionally, DIY methods may not address eggs or nymphs, allowing the infestation to rebound in a short period.
Risks associated with unprofessional pest control
Unprofessional pest control methods can not only be ineffective but also pose risks to individuals’ health and safety. The improper use of insecticides and lack of knowledge about bed bug behavior can lead to overexposure to harmful chemicals or the spread of the infestation to new areas. It is always recommended to seek professional assistance for effective and safe bed bug control.
Effects of improper use of insecticides
Improper use of insecticides can contribute to the development of resistance in bed bugs. Overuse or misuse of insecticides can expose bed bugs to sublethal doses, allowing them to develop resistance over time. Additionally, the over-reliance on insecticides without implementing other control measures can lead to the survival of pesticide-resistant bed bugs, exacerbating the problem further.
Effective Methods for Bed Bug Control
While DIY methods may not be entirely effective, there are various professional pest control services and methods available to successfully eradicate bed bug infestations.
Professional pest control services and their methods
Hiring a professional pest control service is often the best course of action for comprehensive bed bug control. These professionals have the knowledge, experience, and tools to effectively identify and eliminate bed bugs. Professional methods include chemical treatments, heat treatments, and the use of specialized equipment to penetrate hard-to-reach areas and ensure thorough eradication.
Heat treatment and its effectiveness
Heat treatment is an effective method for eliminating bed bugs and their eggs. This method involves raising the temperature of the infested area to a level lethal to bed bugs. Heat treatments can reach all areas of an infested room, including cracks and crevices that may be inaccessible with other methods. It is important to note that heat treatments should be performed by trained professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
Using a mix of control methods successfully
Successful bed bug control often requires a combination of methods tailored to the specific infestation. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approaches combine multiple strategies, such as physical removal, chemical treatments, and preventive measures, to achieve long-term control. By utilizing a mix of control methods, professionals can target both adult bed bugs and their eggs, maximizing the chances of complete eradication.
Preventing Future Bed Bug Infestations
Taking proactive steps to prevent bed bug infestations is essential for maintaining a pest-free environment. By implementing preventive measures and being vigilant, individuals can reduce the risk of infestations and minimize the potential for future problems.
Steps to prevent bed bug infestations
- Regularly inspect your home, particularly beds and other sleeping areas, for signs of bed bugs.
- When traveling, thoroughly inspect hotel rooms and luggage before unpacking.
- Be cautious when acquiring used furniture or clothing, as they may harbor bed bugs.
- Use protective mattress and box spring encasements to prevent bed bugs from establishing themselves in your bedding.
- Clean and vacuum frequently, paying attention to cracks, crevices, and other hiding spots where bed bugs may be present.
- Consider using mattress and box spring covers designed specifically for bed bug protection.
Identifying early signs of infestations
Early detection of a bed bug infestation is crucial for effective control. Some early signs to watch out for include:
- Small blood stains or dark spots on bedding or furniture.
- Dark, rust-colored spots on walls, floors, or other surfaces.
- Presence of bed bug exoskeletons (shed skins) in crevices or hiding spots.
- A distinct, sweet musty odor often associated with large bed bug infestations.
Responsibility of property owners and tenants in prevention
Both property owners and tenants have a responsibility in preventing and addressing bed bug infestations. Property owners should take proactive measures to minimize the risk of infestations, such as regular inspections and maintenance. Tenants, on the other hand, should promptly report any signs of bed bugs to their landlords and take necessary precautions to prevent the spread of infestations.
By working together and staying informed, individuals can help combat the challenges posed by bed bugs and create safer, more comfortable living environments.